Guide to cryptocurrency security
Cryptocurrencies have changed the way people transact digitally. In crypto transactions, no tangible money is exchanged. Instead, financial transactions take place as digital entries to an online database that identify specific transactions. Cryptocurrency transactions are faster and more secure, allowing users to transact without the need of an intermediary financial institution such as a bank.
But, is cryptocurrency secure? The growing popularity of cryptocurrencies has made crypto companies, exchanges, and wallets, an attractive target for cybercriminals. As a result there is a greater emphasis on elevating cybersecurity cryptocurrency to ensure protection for associated platforms and the uses.
In this cryptocurrency security guide, we will take a close look at the importance of security in cryptocurrency, which cryptocurrency is most secure, common cryptocurrency security issues, and how to secure crypto.
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital currency, based on blockchain technology, which allows users to make secure digital payments through tokens. The most common cryptocurrencies in use today include: Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum, Monero, Binance Coin, and so forth.
Cryptocurrency transactions are quick and work on decentralized networks that are independent of any government control. Cryptocurrency exchanges facilitate the purchase of, and trading and investing in cryptocurrencies.
What is cryptocurrency security?
The measures taken to secure crypto transactions from fraudulent activities and maintain digital currency security is called crypto currency security. In addition to requiring username and verification code for the first use, crypto exchanges use blockchain and cryptography techniques to enhance crypto cybersecurity, make transactions safer, and stop cryptocurrency fraud.
Cryptocurrency transactions are digital in nature and follow a complex backend process. The technology behind cryptocurrency security is blockchain which is essentially a distributed database or ledger that is shared between a number of computer network's nodes. Blockchain provides comprehensive risk management against cyber threats using cybersecurity frameworks and best practices. Cryptography protects information and communication and uses codes to ensure only authorized persons can use them.
Which cryptocurrency is most secure?
Ethereum is considered to be the most secure cryptocurrency as compared to other digital assets. This is largely because its platform uses the blockchain technology, which is one of the most robust technologies for digital transactions.
Further, to enhance security of the platform, Ethereum uses the proof-of-stake consensus method, which deters bad actors by not providing any means to exploit or control the network.
Common cryptocurrency security issues
In recent years, cryptocurrency has gained popularity, with a large number of consumers using them. This growing popularity has attracted the attention of bad actors, who engage in numerous scams and fraudulent activities.
Fraudulent investment opportunities, illegitimate crypto platforms, crypto mining security risks, fake wallets, and so forth are some of the most common forms of cryptocurrency security issues prevalent in the cryptocurrency segment. Let’s take a closer look at some of the issues in the world of cryptocurrency:
- Phishing: Bad actors create fake websites or send emails posing as legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges or wallet providers to trick users into sharing their login credentials, seed words, or private keys. Sometimes clicking a link may lead to crypto mining security risks. Here, a cryptocurrency mining code may get loaded on users’ computers, mining cryptocurrency for the attacker, while the victim may only see their computers slowing down.
- Ponzi Schemes: Cybercriminals float fake schemes wherein they promise high returns on investment and rely on new investors' funds to pay out earlier investors. Eventually, in the absence of enough new investors to sustain the scheme, it collapses.
- Fake Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs): By launching fake ICOs, offering new tokens or coins in exchange for investments, bad actors dupe unsuspecting users. Attackers create professional-looking websites to attract investors and disappear as soon as they have collected funds.
- Pump and Dump Schemes: In this scam, bad actors artificially inflate the price of a low-volume cryptocurrency through false or misleading information. They then sell it at the peak to make a profit, causing significant losses to the investors. Often, attackers form groups on messaging apps and social media platforms to execute these schemes.
- Fake Wallets and Exchanges: By creating malicious yet genuine-looking wallets or exchanges, bad actors steal users' funds or personal information. They advertise their fraudulent wallets on popular search engines and social media platforms to gain traction. If a user clicks the ad and visits the website, they are redirected to a link to download a legitimate copy of the software. However, this software is tampered with and designed to send the seed words to the fraudster. The crypto transaction that the user completes goes to the attacker’s wallet instead of the users’.
- Social Media Giveaway Scams: In this type of fraud, cybercriminals impersonate prominent public figures on social media platforms and promise to give away cryptocurrency. To receive the freebies, users must send a covering fee in cryptocurrency or to verify their identity. However, the promised giveaway never happens.
- Malware and Ransomware Attacks: This is a method to gain access to users' computers or mobile devices by planting malicious software and then stealing their cryptocurrency or encrypting their data and demanding a ransom to release it.
- Double-Spend Attacks: Here, an attacker may be able to spend their own crypto and then erase the transaction.
How is cryptocurrency secure?
If centralized networks have a security flaw, attackers can access a user’s account. However, it is nearly impossible for an attacker to hack into a crypto network that is decentralized. This is because attackers cannot steal a user’s crypto without gaining access to their private key.
The prime reasons why it is difficult to breach cybersecurity in cryptocurrency are as listed below:
- Balance: The several nodes on a cryptocurrency network have a copy of the database. In an instance, an attacker is successful in altering the balance on one node, it will be different from the balances on the other nodes. This creates an anomaly which results in the rejection of the balance shown in the compromised node.
- Signatures: Valid signatures are a prerequisite for every transaction. If a node approves a transaction, the other nodes too would need the signature to pronounce the transaction as valid. However, if the signature is not produced, the other nodes will reject the transaction.
- Protection: Crypto security prohibits double-spend attacks, which involve compromising a node that must display a transaction history longer than all the other nodes, by making these attacks expensive with investments, often far exceeding the potential returns.
What are cryptocurrency security standards?
The requirements specified for the use of cryptocurrency systems, including cryptocurrency exchanges, mobile, and web applications, are collectively called Cryptocurrency Security Standards. These standards help manage and standardize the techniques as well as improve crypto currency security.
There are ten key points specified in the Cryptocurrency Security Standards (CCSS) that most cryptocurrency exchanges use while setting up cryptocurrency security systems. The key steps aligned with the Cryptocurrency Security Standards include: key/seed generation, wallet creation, key storage, key usage, key compromise policy, keyholder grant/ revoke policy and procedures, third-party audits, data sanitization policy, proof of reserve, and log audits.
How cryptography improves cryptocurrency security
Cryptography is a technique that helps protect cryptocurrency by securing information and communication by authenticating a transaction. While creating a wallet, a ‘hash’ unique to that wallet is generated.
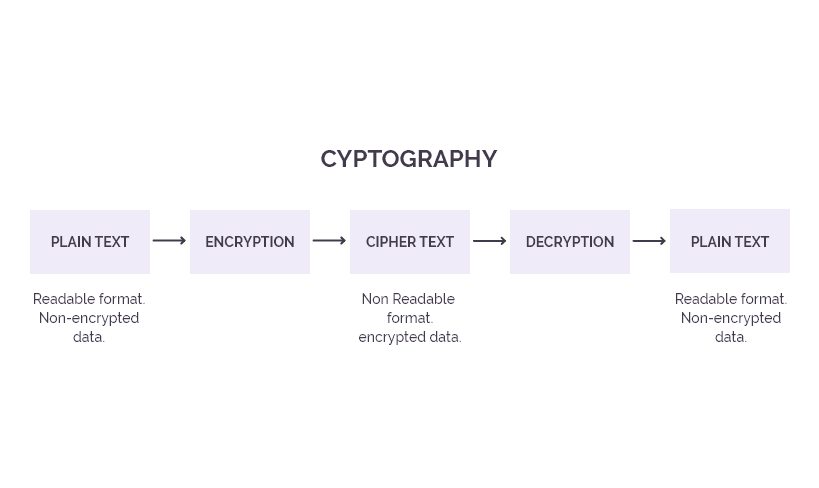
During a transaction, a hash gets transmitted with encrypted information about the receiver’s address and the amount being transferred. It is also signed with the sender’s private key. For completion of the transaction, not only must the receiver provide the public key generated by the sender’s wallet but all other information must also match.
Ways to enhance crypto security
Cryptocurrencies hold immense monetary value, which makes them attractive to attackers. As explained earlier, there are many ways attackers may target cryptocurrency security systems.
To prevent attackers from exploiting their platforms, causing losses, and disrupting the digital experience of genuine users, cryptocurrency companies must consider ways to strengthen cryptocurrency cyber security. They must take proactive action to ensure security of their platforms and their customers’ accounts. Here are some steps that they may consider implementing:
- Risk Assessment: It is critical to conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities, threats, and risks specific to the cryptocurrency business, as well as to prioritize the mitigation efforts.
- Private Key Protection: Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic keys, specifically private keys, to access and control ownership of digital assets. Protect private keys using techniques such as encryption, secure storage, and hardware wallets.
- Wallet Security: Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA) and regular updates to wallet software are key to improving wallet security.
- Two Factor Authentication: Deploy 2FA to add an extra layer of security to cryptocurrency accounts.
- Secure Transactions: Verify recipient's wallet address using additional security features like transaction signing and encryption.
- Network Security: Use cryptographic algorithms and network monitoring to protect the blockchain infrastructure from bot-driven attacks such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Implement firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs), strong encryption and regular patching and updating of network devices.
- Crypto Exchange Security: Exchange security includes measures to protect user accounts, secure storage of assets, two-factor authentication (2FA), anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures, regular security audits, and adherence to regulatory standards. Enable additional security features like withdrawal whitelists or IP restrictions, and practice due diligence when selecting trading partners.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data, both in transit and at rest using several available encryption techniques to protect data from unauthorized access or interception.
- Smart Contract and Token Security: Follow secure coding practices and ensure proper testing before deployment.
- Strong Password Practices: Provide guidelines for creating robust passwords and recommend the use of password managers to securely store and manage credentials.
- Access Control and User Privileges: Implement strong access controls and user privileges to restrict access to sensitive data and systems.
- Software and Firmware Updates: Regularly update cryptocurrency wallets, software clients, and firmware for hardware wallets, as these updates may contain security patches and improvements for improved protection from known threats.
- Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up cryptocurrency wallets and store the backup securely.
- Continuous Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring of cryptocurrency security systems and networks is essential to detect and respond to potential security breaches or suspicious activities. Use monitoring tools, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection systems, and threat intelligence feeds to identify and mitigate security incidents.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Have an incident response plan in place – complete with procedures for reporting and analyzing incidents, containment and mitigation of damages, recovery of lost funds (if possible), and improving security measures to prevent future incidents – for instantaneous response to security incidents.
- User Education and Awareness: Educate cryptocurrency users about best security practices, common attack vectors, and potential risks such as phishing attempts, social engineering techniques, and the importance of maintaining personal security hygiene, including use of strong passwords, regular software updates, and not sharing sensitive information.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with jurisdiction-specific regulations such as those related to anti-money laundering (AML), counter-terrorism financing (CTF), and data protection.
- Partnering With a Security Vendor: Choose a reliable security vendor after evaluating security measures, such as data handling, access controls, and incident response capabilities.
- Security Audits and Assessments: Conduct periodic security audits and assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of security measures and identify any gaps or weaknesses. Consider engaging third-party experts to conduct audits for an objective assessment of the overall security posture.
Upgrade crypto security with Arkose Labs
Arkose Labs protects leading cryptocurrency platforms from the onslaught of automated bot attacks with an innovative approach that deters attackers, while maintaining great user experience for genuine users.
By diverting the traffic to its own network, Arkose Labs creates a protective shield between the attackers and the client who can continue with business activities as usual, while Arkose Labs takes on the attackers. After the incoming traffic is triaged using a number of tests, targeted friction in the form of Arkose Matchkey challenges is presented to suspicious users. Non-human traffic comprising bots, software scripts, and automatic solvers fail instantly as they are no match to the highly resilient Matchkey challenges.
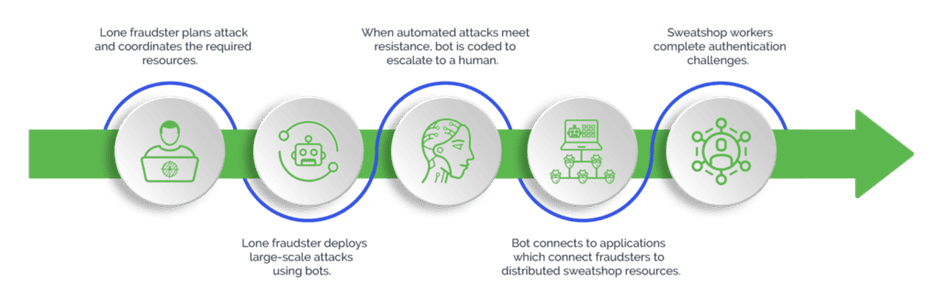
Even when attackers use a hybrid model and leverage persistent malicious humans or click farms to attack, they stand no chance to solve these challenges at scale. This is because there are thousands of variations for a single challenge, which would sap time, effort, and resources trying to automate solving each of the individual challenges. Mounting investments mean depleting returns, which makes the attack not worthwhile to pursue any further. As a result, attackers give up and move on for good.
As a true partner, Arkose Labs also provides 24x7 support along with actionable insights, raw signals, attributes and data points to enable security teams to fend off growing threats with confidence and ensure long-term protection for their business and customers against new and evolving attack techniques.