Fraudulent activities in eCommerce can take many forms, such as identity theft, account takeovers, phishing scams, or chargeback fraud, and can result in significant financial losses for businesses and consumers alike. It is a broad term that covers any type of fraudulent activity related to online shopping. This type of fraud can be costly for merchants, as they have to issue the refund and also deal with the returned item.
eCommerce fraud is now a significant problem for online retailers and consumers alike. Criminals use a variety of tactics to obtain goods or services from online merchants without paying for them, causing financial losses and damage to the reputation of the affected businesses. In this context, it is essential to be aware of the different types of ecommerce fraud that can occur.
What is ecommerce fraud?
Fraud in retail and ecommerce refers to the act of using illegal or deceitful practices to obtain goods or services from online retailers, with the intent of not paying for them. This type of fraud can occur at any stage of the transaction process, from the initial order to the final payment. eCommerce fraud is a significant issue for online retailers, as it can result in substantial financial losses and damage to their reputation.
There are various types of ecommerce fraud that online retailers must be aware of, including stolen credit card numbers, fake identities, and fraudulent payment methods. That said, one of the most common is through password theft. This happens when a fraudster obtains customer information, including passwords and account details. Once attackers have this information, they can perform account takeover fraud and make purchases, withdraw funds, or access other accounts owned by the user.
Cybercriminals rely on other scams to obtain sensitive information from unsuspecting customers, which they can then use to commit fraud. In some cases, criminals may even use bad bots or other automated tools to carry out fraudulent activities, making it difficult for online retailers to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions.
Types of eCommerce fraud
Online fraud within ecommerce can take many forms, from stolen card information to identity theft and chargeback fraud. As the ecommerce industry continues to expand, so does the risk of cybercrime. It is important for businesses to understand the different types of ecommerce fraud, how they occur, and what measures they can take to protect themselves and their customers.
Fake website fraud is a type of scam in which a fraudster creates a website that mimics the appearance of a legitimate business site, but is actually designed to trick card holders into entering their personal details. Scammers can collect sensitive financial information and use it for fraudulent purposes. It is essential to be vigilant when browsing the internet, particularly when making online purchases.
Phishing happens when scammers send out emails or other types of communication that appear to originate from a legitimate business or organization—but these messages are actually attempts to deceive the recipient into providing their personal information, such as payment card details.

Account takeover fraud takes place when a scammer uses stolen login credentials to gain access to an individual's or business's online account. With account takeover fraud, once the threat actor has access, they can make unauthorized transactions or changes, causing financial losses and potentially damaging the victim's reputation.
Stolen credit card fraud involves the use of stolen credit card information, obtained through phishing scams or data breaches. Bad actors make bogus purchases online using this information. Retailers can use payment gateway filters and other fraud detection software to protect themselves from this type of fraud.
Identity fraud involves the use of fake identities to obtain goods or services online. Criminals can create fake accounts using stolen personal information or bots to generate accounts. They can make fraudulent purchases or steal sensitive information using legitimate accounts. Retailers can use fraud detection software and verify customer identities to protect themselves from this type of fraud.
Friendly fraud happens when a customer disputes a legitimate transaction, claiming it was unauthorized or fraudulent. Although the customer may be acting in good faith, this type of fraud can result in financial losses for the retailer.
Card testing fraud happens when fraudsters test stolen credit card numbers by making small purchases. Card testing fraud can be prevented by implementing best practices, such as checking for suspicious activity, being aware of red flags, and monitoring cardholder data.
Refund abuse is a growing concern for online merchants. Refund abuse occurs when customers return broken, damaged, or even stolen items to a retailer in exchange for a refund. Scammers may use various tactics, such as buying a product with the intention of returning it after use, swapping out the original product with a defective or damaged one, or even returning stolen merchandise for a refund.
Refund abuse can result in significant losses for businesses, as they are essentially giving away products or refunds without receiving the intended benefit of the sale. In addition to financial losses, refund abuse can also lead to a decline in customer trust and brand reputation, as customers may become dissatisfied with the quality of products or the customer service offered by the retailer.
Interception fraud occurs when fraudsters purchase goods from an online retailer using a stolen credit card—but avoid certain checks by providing legitimate, matching shipping and billing addresses. Upon placing the order, the goal is to intercept the package before it gets to the address provided.
Triangulation fraud involves a legitimate customer, a legitimate online store, and a fake online store operated by a fraudster. Triangulation fraud can be difficult to detect, as the fake store may appear to be legitimate. However, there are some signs to look for, such as cheap goods or promotions that seem too good to be true.
Warning signs of eCommerce fraud
eCommerce has revolutionized the way businesses operate, enabling them to reach a broader customer base and increase revenue. However, the rise of online retail has introduced corresponding fraud. Bad actors are constantly coming up with new and sophisticated ways to cheat businesses out of their hard-earned profits. That is why it is crucial for businesses to stay alert to the warning signs of ecommerce fraud to avoid falling victim to it.
Here are a few key indicators to look out for:
Unusual or large orders are often a sign of online fraud because fraudsters tend to place larger orders in order to maximize their profits. These orders may include multiple high-value items, which they can resell at a profit. In some cases, fraudsters may use stolen credit card details to make large purchases, hoping that the business will not notice the discrepancy until it is too late.
Scammers may also use this tactic as a way to test the waters before placing even larger orders in the future. By placing an unusually large order and seeing if it goes through without issue, they can gain confidence in their ability to defraud the business and may attempt even larger orders in the future. As a result, businesses should always be wary of orders that are significantly larger than usual, and take the necessary steps to verify the authenticity of the order before fulfilling it.
Unusual shipping or billing addresses can also indicate ecommerce fraud. Attackers use the information of a cardholder to place orders and have the items shipped to a different address than the billing address associated with the card. This is why businesses should be wary of orders that have different shipping and billing addresses, particularly if they are in different countries.
Bad actors can also target businesses that ship to international addresses, as this makes it more difficult for the business to verify the authenticity of the order. In some cases, the shipping address may even be a vacant property or a temporary mailbox set up by the fraudster.
Unusual payment methods such as a gift card or a cryptocurrency can indicate signs of ecommerce fraud. Gift cards are a popular payment method among fraudsters because they are difficult to trace and can be resold for cash. In some cases, threat actors may use a stolen card number to purchase gift cards, which they can then use to make purchases from the business.
Cryptocurrencies are also becoming an increasingly popular payment method among fraudsters because they offer a degree of anonymity and are difficult to trace. Attackers may use stolen credit card information to purchase cryptocurrencies, which they can then use to make purchases from the business.
Rushed or overnight shipping is often requested by scammers looking to minimize the time available for the business to detect and prevent the fraud. By requesting this type of shipping, scammers hope to receive the merchandise as quickly as possible, which gives the business less time to detect and prevent unauthorized activity.
This tactic is particularly effective in cases where the business does not have a robust fraud detection system in place. In some cases, attackers may even go as far as to provide false shipping information to make it more difficult for the business to track the package and recover the merchandise.
Suspicious IP addresses, particularly those from high-risk countries or ones known for fraudulent activity, can be a sign of ecommerce fraud. IP addresses are unique identifiers that can provide information about the location of the device used to place the order. Some fraudsters use virtual private networks (VPNs) or other anonymizing services to conceal their true location and make it more difficult for businesses to identify potential fraud.
Repeated Attempts to place an order using the same credit card or shipping address can be a red flag for ecommerce fraud. Fraudsters often use this tactic to try different combinations of information in the hopes of getting an order through undetected.
Businesses should be cautious of multiple attempts to place an order using the same credit card or shipping address, especially if the attempts are coming from different devices or IP addresses. This could be a sign that the fraudster is using a botnet or other automated tool to try and bypass fraud detection systems.
How to prevent eCommerce fraud
Online vendors can rely on various tools and techniques to combat fraud, such as advanced detection software, payment gateway filters, and customer identity verification. Third-party services that specialize in fraud prevention may also be employed. These measures help retailers identify and prevent fraudulent transactions, protecting their revenue and reputation.
There are several measures that businesses can take to prevent ecommerce fraud, including:
- Fraud detection software uses machine learning algorithms to analyze customer behavior and identify fraudulent transactions.
- Payment gateway filters can be used to block transactions from high-risk countries, prevent certain types of transactions, and set up rules for transactions that require further verification.
- Customer identities should be verified by businesses through methods such as two-factor authentication or by requesting government-issued identification.
- Monitor transactions regularly to detect and prevent ecommerce fraud. This includes analyzing transaction patterns, verifying shipping addresses, and tracking IP addresses.
- Third-party services that specialize in cybercrime prevention can help businesses identify and prevent fraudulent transactions.
- Educate customers on how to protect themselves from ecommerce fraud, such as by using secure payment methods, verifying the authenticity of websites, and being cautious of unsolicited requests for personal or financial information.
Ecommerce fraud prevention tools can help you protect your business against fraudsters. Data enrichment can help you build a complete profile of customers, while email authentication can help prevent fake accounts and purchases.
By implementing these measures and maintaining a vigilant attitude, online merchants can significantly reduce the risk of ecommerce fraud, thereby safeguarding their revenue and reputation. However, it is important to note that preventing ecommerce fraud is not just the responsibility of businesses alone, as customers also play a crucial role in preventing these threats. In this way, preventing ecommerce fraud is a joint effort between online retailers and their customers, with retailers taking proactive measures to detect and prevent fraudulent activity and customers remaining vigilant in protecting their personal and financial information.
How Arkose Labs fights ecommerce fraud
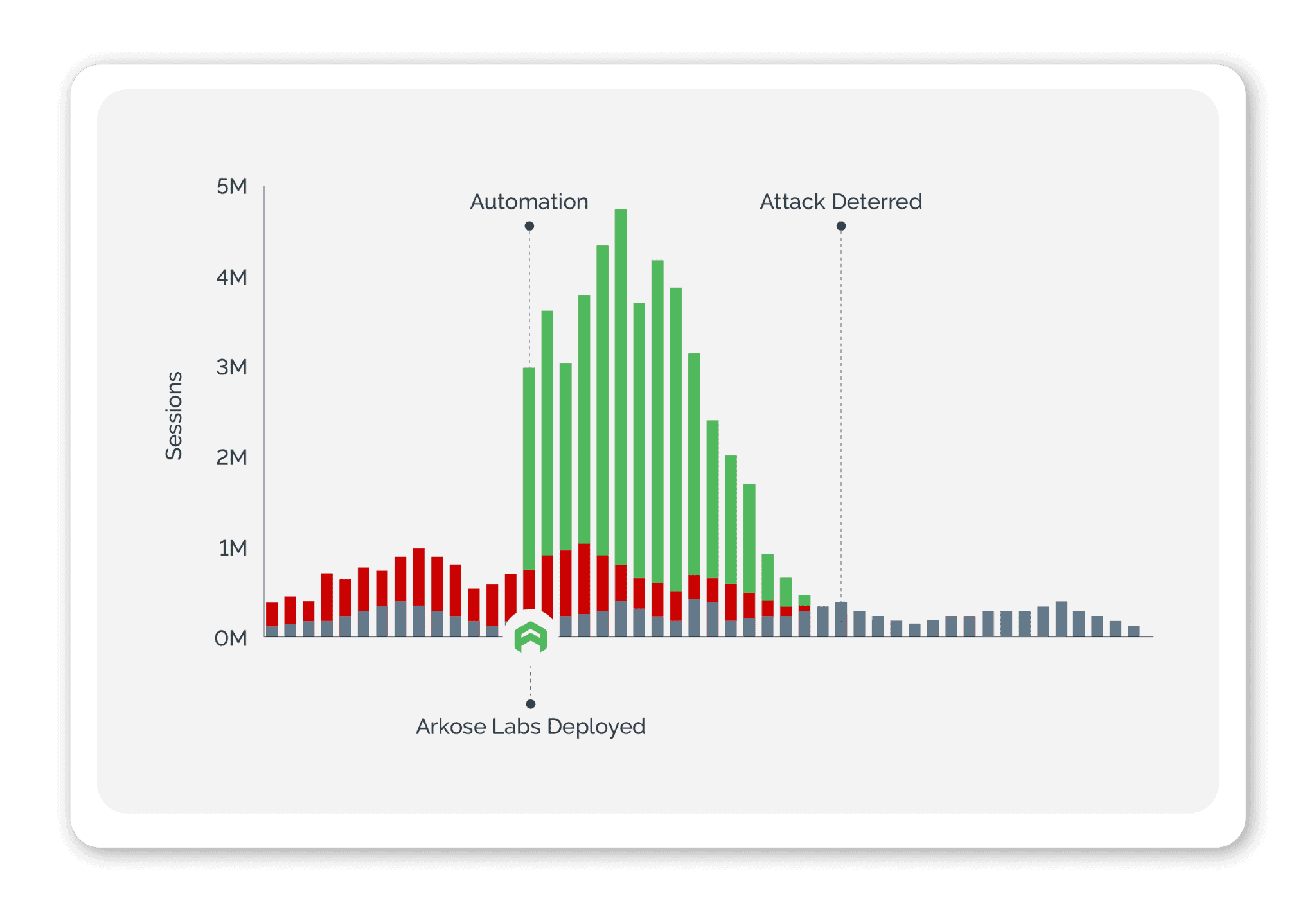
Arkose Labs provides ultimate protection and fraud prevention for the long-term. Our AI-driven platform is designed to combat persistent bots and human attacks that target user touch points on websites and applications. The invisible risk assessments from our technology allow genuine customers to pass through without even realizing it, while high-risk traffic is identified and enforced with difficult challenges that discourage any future attempts. This ensures a secure experience for all users, while also deterring any malicious attacks. Our AI-powered platform is constantly adapting to the ever-changing landscape of cyber security threats, allowing us to deliver the highest level of protection and fraud deterrence.
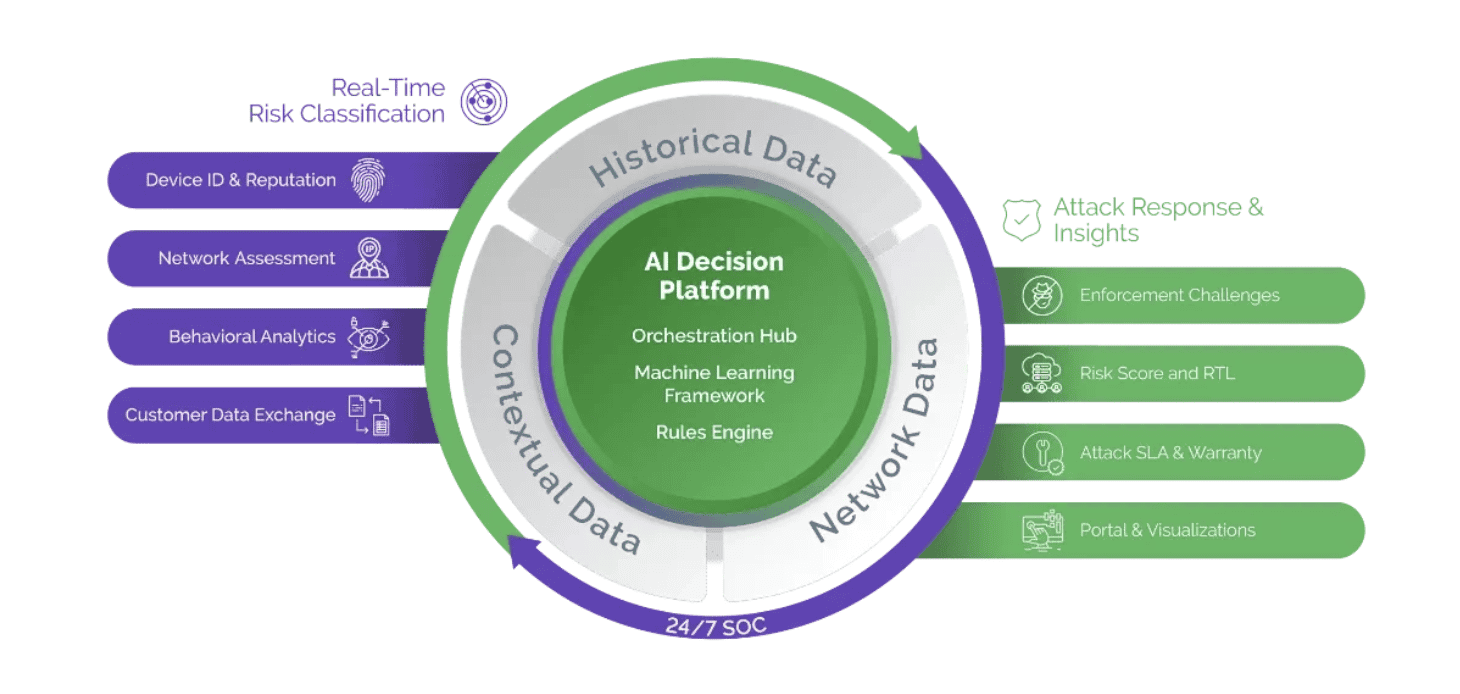
The Arkose Labs platform utilizes an AI-driven decision engine to process real-time signals combined with deep historical intelligence to create a targeted attack response. It identifies and detects evolving attack techniques while allowing legitimate users to pass through security checkpoints with ease. This decision engine is continuously learning from real-time assessments and challenge interaction data, enabling it to accurately and effectively protect against new threats. This adaptive approach ensures that the platform is able to proactively respond to changes in attack techniques and is always one step ahead of malicious actors.