What is advanced phishing?
Advanced phishing is a sophisticated attack that uses social engineering and legitimate websites to launch cyber attacks fast, at scale. It deceives consumers into sharing login information, MFA codes, and other details to a malicious reverse proxy website. Attackers submit that information to legitimate websites and take over consumers’ accounts.
What Is the Role of Reverse Proxy Sites in Advanced Phishing Attacks?
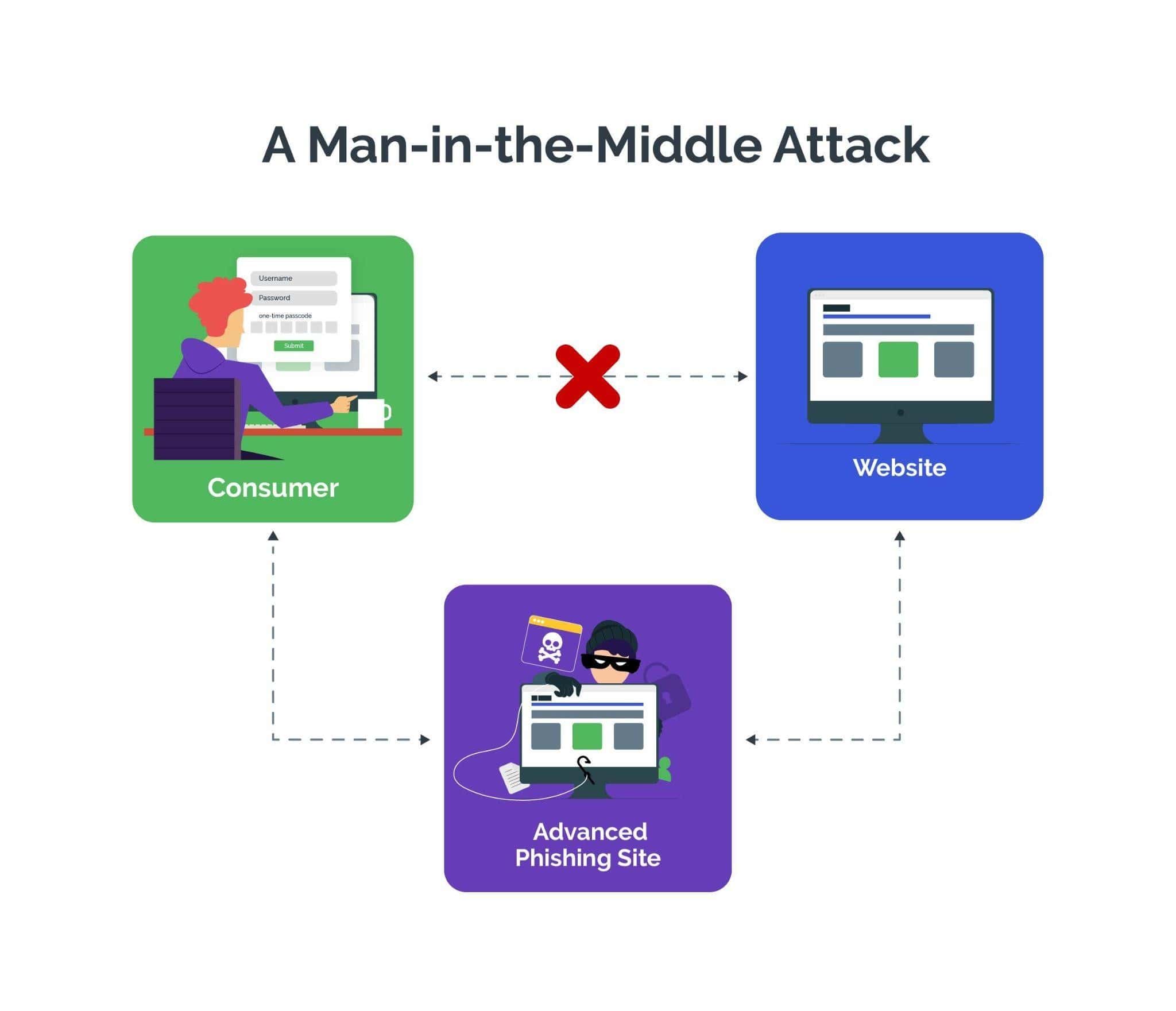
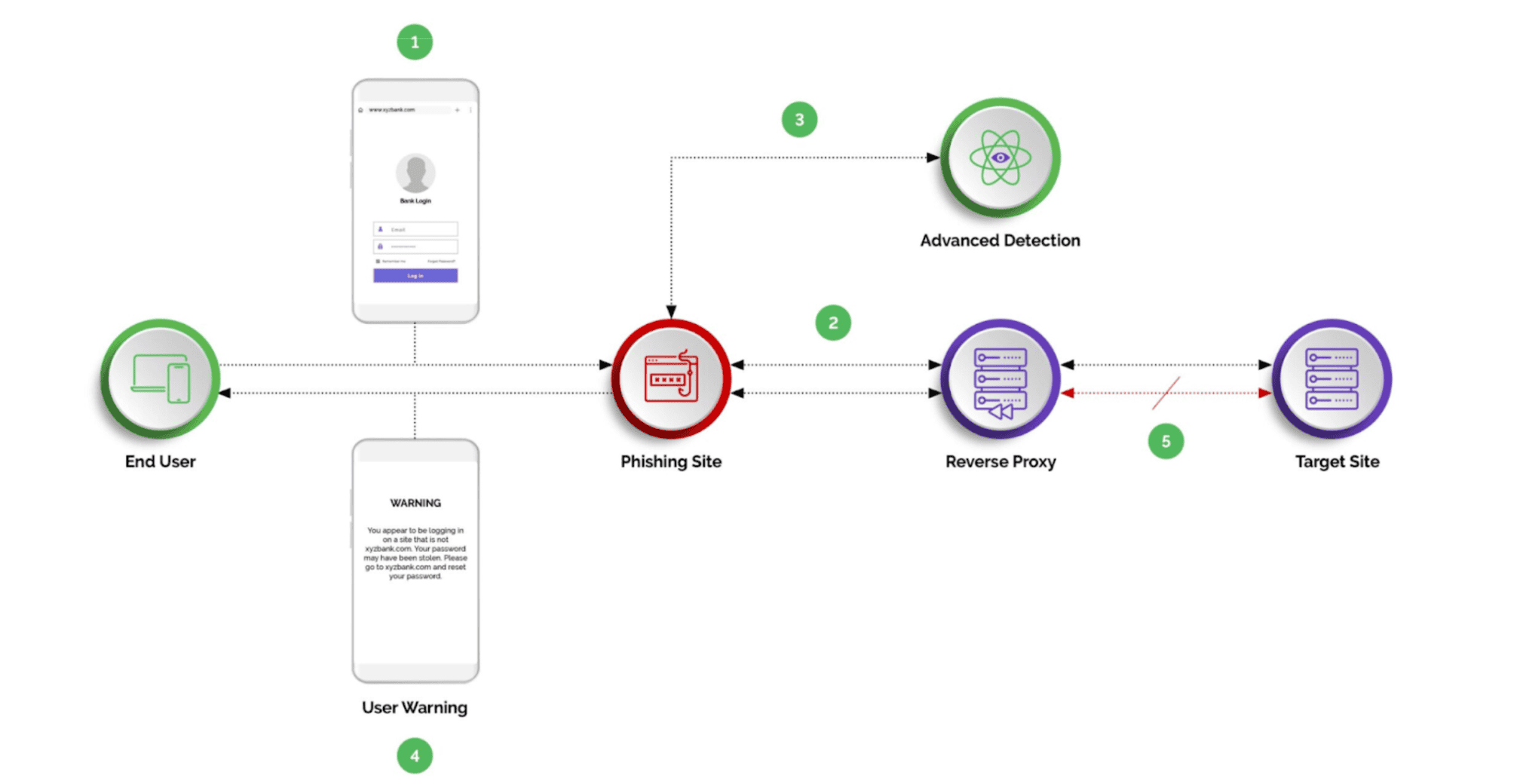
Reverse proxy sites facilitate advanced phishing attacks, also called man-in-the-middle attacks or MITM attacks, by serving as intermediaries between unsuspecting users and malicious servers. These fake sites spoof legitimate websites with malicious URLS that closely mimic legitimate sites. This misleads users into believing that they are interacting with the real site so that they readily disclose sensitive information, such as username and password.
Proxy sites hide the true origins of phishing campaigns, obscure the attacker's infrastructure, and evade traditional cybersecurity measures to make it harder for security teams to detect.
How Advanced Phishing Attacks Work
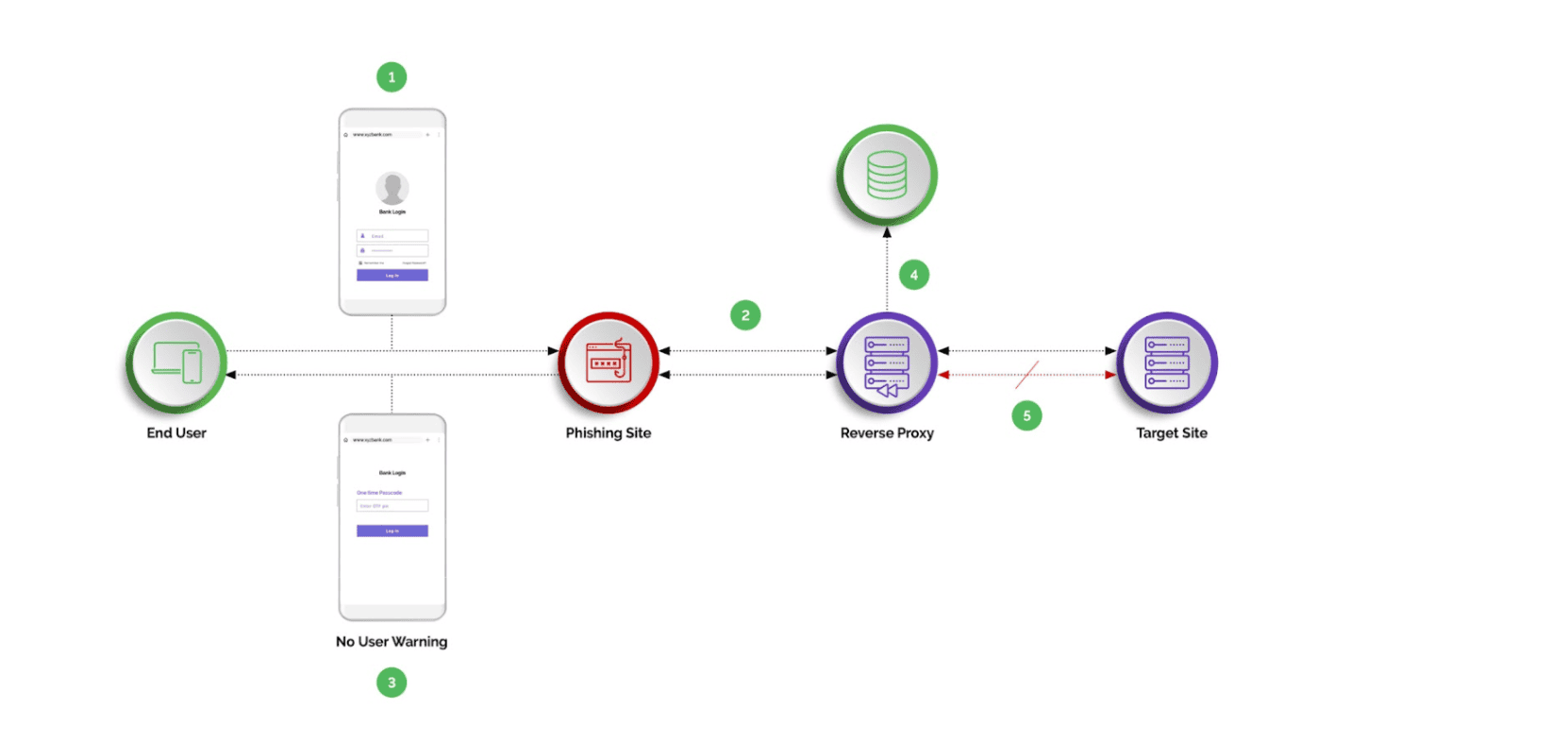
Advanced phishing attacks involve attackers setting up reverse proxy servers to act as an intermediary between the user and a company’s real website. Although the users believe they are interacting directly with the legitimate site, in reality their requests pass through the attack server.
To execute man-in-the-middle attacks, bad actors may register a domain name similar to the real one, such as one with a slightly misspelled version of the domain name, which are often overlooked. Attackers may even choose to obtain SSL/TLS certificates for their fraudulent domains to give the impression of a secure connection and make the reverse proxy attacks more believable.
When users access these proxy sites, their requests are intercepted and forwarded to the company’s legitimate website, while the attacker collects sensitive information such as account information, username, passwords, OTP (one-time passcode) or other sensitive information.
Involvement of Bad Actors
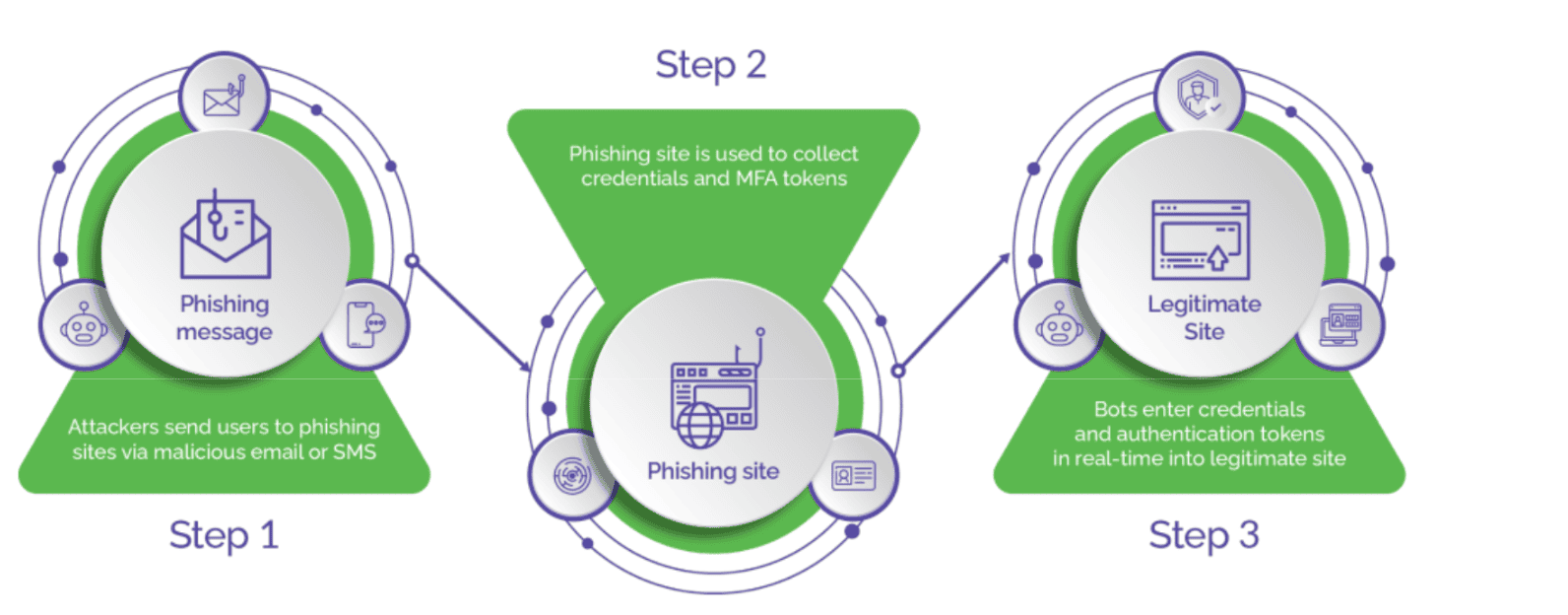
Advanced phishing attacks are generally executed by bad actors, who are skilled cybercriminals or organized hacker groups. These bad actors leverage their expertise to craft sophisticated campaigns by researching targets and employing social engineering tactics to create convincing phishing emails and apps that appear legitimate.
Hackers set up infrastructure for MITM attacks, which includes scripts, web servers, storage to collect user credentials, and templates for creating fake emails, apps, and phishing sites. Experts hackers make money by offering phishing-as-a-service (Ph-a-a-S) to bad actors with little or no technical skills at a fee.
Understanding the Automated Bots
Automated bots streamline various stages of the advanced phishing attack process, including research, message distribution to target email addresses, and response collection. These bots can crawl the internet to gather information about potential targets, identify vulnerabilities, and automate the creation of convincing phishing messages tailored to individual victims.
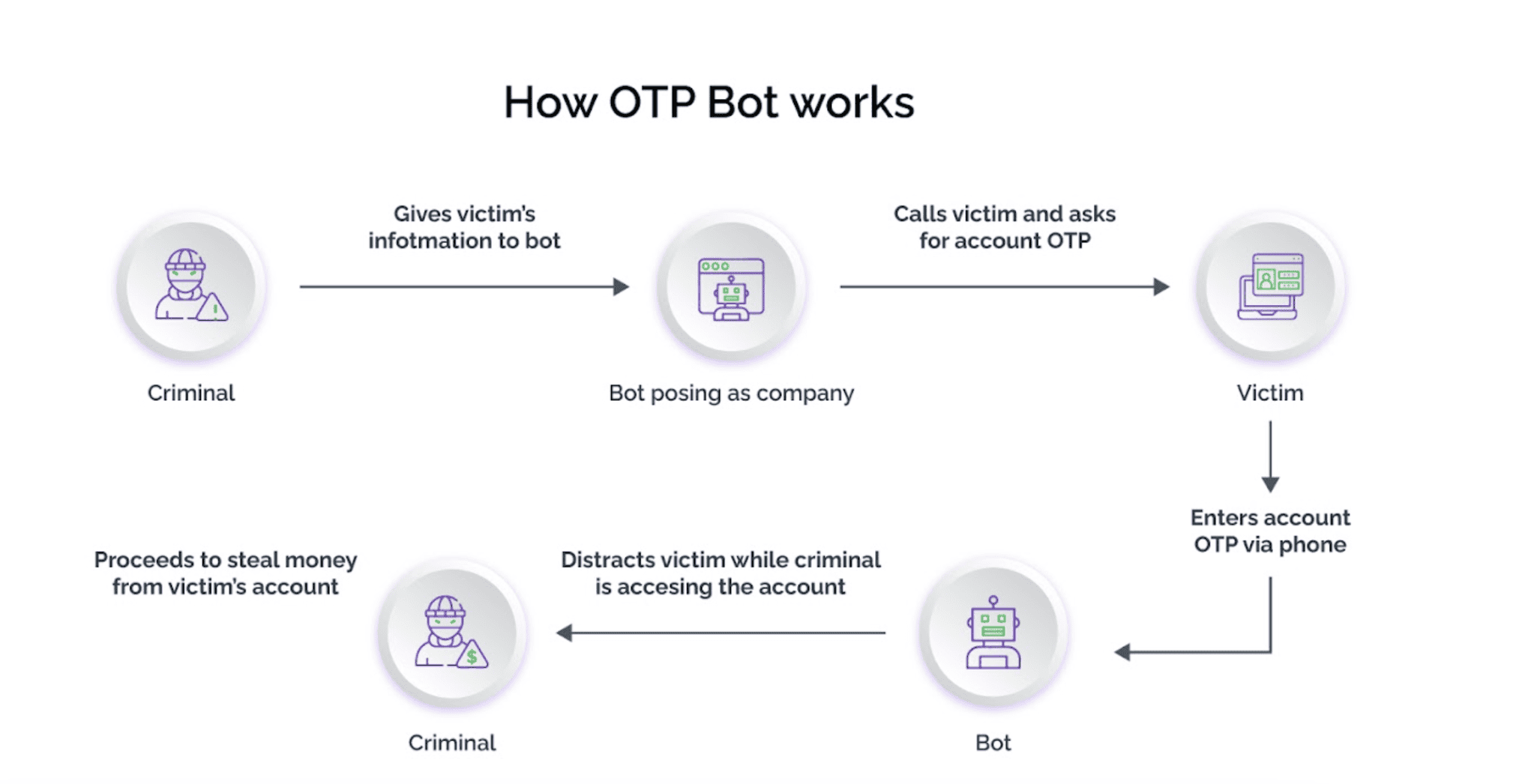
Using automated bots, attackers can collect and analyze responses efficiently, allowing them to refine their scam tactics and launch more effective attacks in future. Specialized OTP bots can intercept OTPs sent out to users for multi-factor authentication (MFA) and exploit them to compromise users account security and gain unauthorized access. Furthermore, using spoofing and other tactics, intelligent bots can fool defense measures by mimicking human behavior, resulting in the compromise of sensitive information or the infiltration of corporate networks.
What Are the Risks Associated With Advanced Phishing Attacks?
Advanced phishing attacks pose significant risks to consumers and businesses, including financial losses, data breaches, account takeover, and damage to reputation.
Implications for Enterprises
In addition to financial losses, in the form of costs of remediation, advanced phishing attacks can damage brand reputation and lead to legal repercussions for affected businesses.
Breaches resulting from these MITM attacks may expose sensitive corporate data, including customer information and intellectual property. This can jeopardize user trust and revenue generation opportunities as well as expose the business to regulatory fines and potential litigation.
Risks for End Customers
Advanced phishing attacks can result in financial fraud, identity theft, and loss of personal information for end customers, causing financial hardship and emotional distress.
By attacking collaboration channels, such as browsers, apps and websites that customers often use, hackers can use reverse proxy attacks to harvest credentials, compromise user accounts, perform unauthorized transactions, and steal sensitive information such as passwords and financial information.
How to Detect Advanced Phishing Attacks
Businesses must adopt a multi-faceted approach that allows identification of fake and proxy websites using their look and brand name.
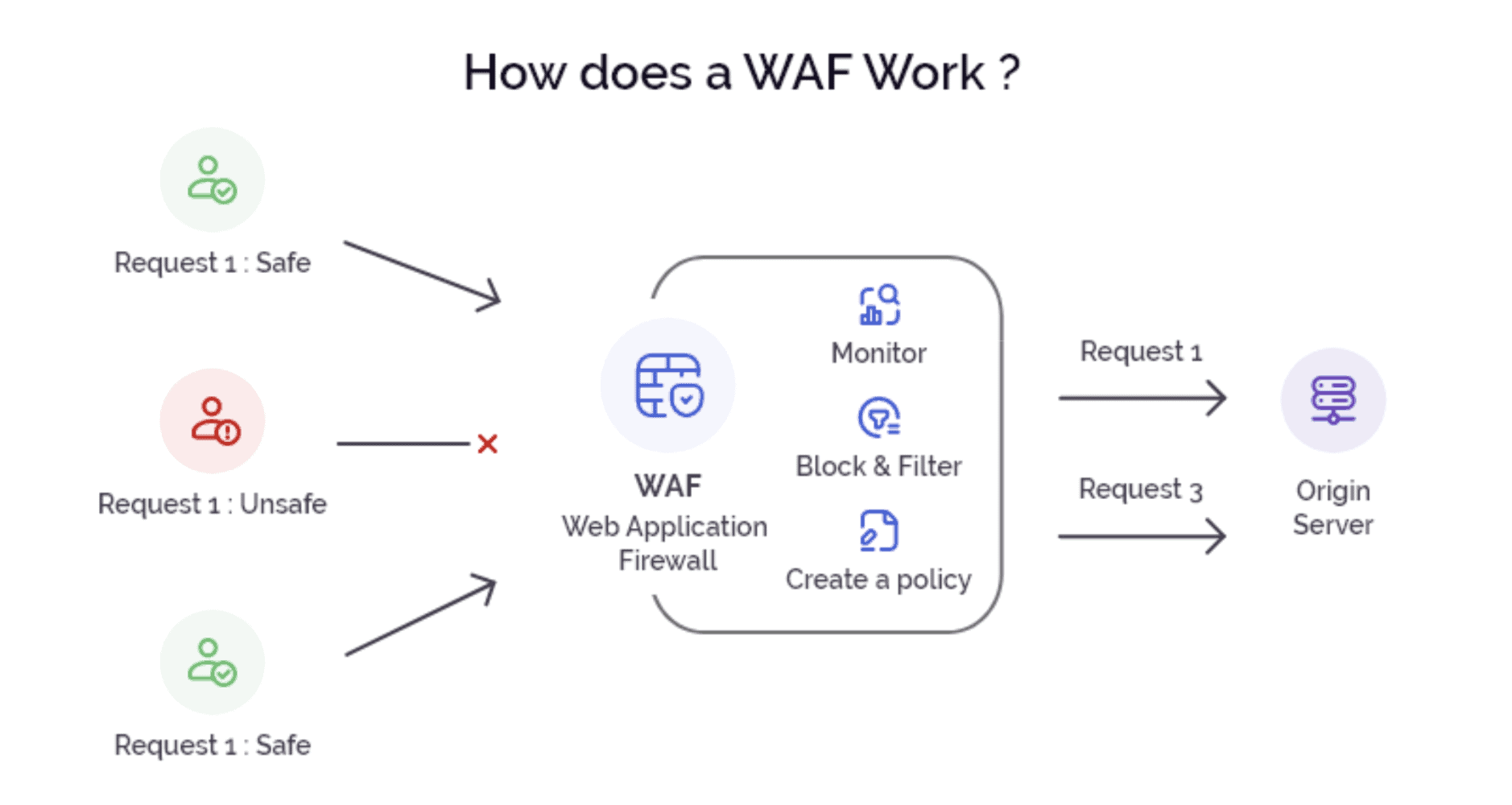
In addition to continuous monitoring for effective email security, businesses must deploy web application firewalls and AI-driven smart solutions such as Arkose Phishing Protection. Businesses must conduct regular training to enable users to identify and quarantine suspicious emails, avoid clicking malicious links or downloading any email attachments in incoming emails, and keep their inbox free from junk emails. These measures can effectively halt phishing attempts based on known indicators or anomalous behavior and safeguard against the manipulation of login and MFA credentials.
Signs to Look Out For
Signs may include:
- Theft of highly protected accounts
- Discrepancies in the displayed URL or domain name
- Clones of the company's website
- Spoofed sender email addresses
- Interception of sensitive information transmitted over insecure connections
- Injection of new host header
- Unexpected SSL certificate warnings
- Unusual network behavior such as slow connections or frequent disconnections
- Suspicious changes in the behavior of devices or software, such as unexpected prompts for login credentials or modifications to encrypted communication settings
- Unexpected redirections to unfamiliar or malicious websites
How To Prevent Advanced Phishing Attacks
To prevent advanced phishing attacks, organizations must employ several strategies that focus on robust security and active threat detection:
- Encryption: Safeguards sensitive data in transit, reducing the risk of interception.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds layers of security to verify user identities.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Secures communications through strong authentication.
- Endpoint Security: Ensures devices are protected against unauthorized access.
- Ongoing Cybersecurity Assessments: Regular evaluations to identify vulnerabilities and strengthen defenses.
- Utilizing MITM Detection Software: Detects and blocks adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) and reverse-proxy phishing attacks. Secures MFA by preventing interception of codes and tokens, and provides real-time alerts for proactive threat response.
H2: How We Can Help Combat Man in the Middle Reverse Proxy Attacks
We provide tailored solutions to defend your organization against sophisticated phishing threats, such as adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) and reverse-proxy attacks. Our advanced MITM detection technology delivers real-time monitoring, secures multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems, and blocks the interception of essential codes and tokens. By offering proactive threat alerts, we enable businesses to respond promptly and protect sensitive information, ensuring unauthorized access is prevented and customer data remains secure.
Request a demo to discover how our advanced phishing protection can enhance your security.