The online commercial banking industry is facing a growing risk from pervasive man-in-the-middle (MITM) phishing attacks. These attacks slip past unsuspecting consumers and financial services as they ravage financial systems and personal security.
Just how hidden are these threats? One of our customers flagged a staggering 175,000 man-in-the-middle phishing sessions during the initial deployment of our MITM protection software — attacks that had previously gone unnoticed.
We are witnessing firsthand the evolution of advanced phishing attacks in both sophistication and frequency. In fact, 46% of attacks on financial organizations involve some form of phishing. Understanding the techniques of man-in-the-middle phishing, a significant risk that demands attention, will arm your finserv business with the knowledge necessary to fortify defenses.
When Man-in-the-Middle Phishing Sites Attack
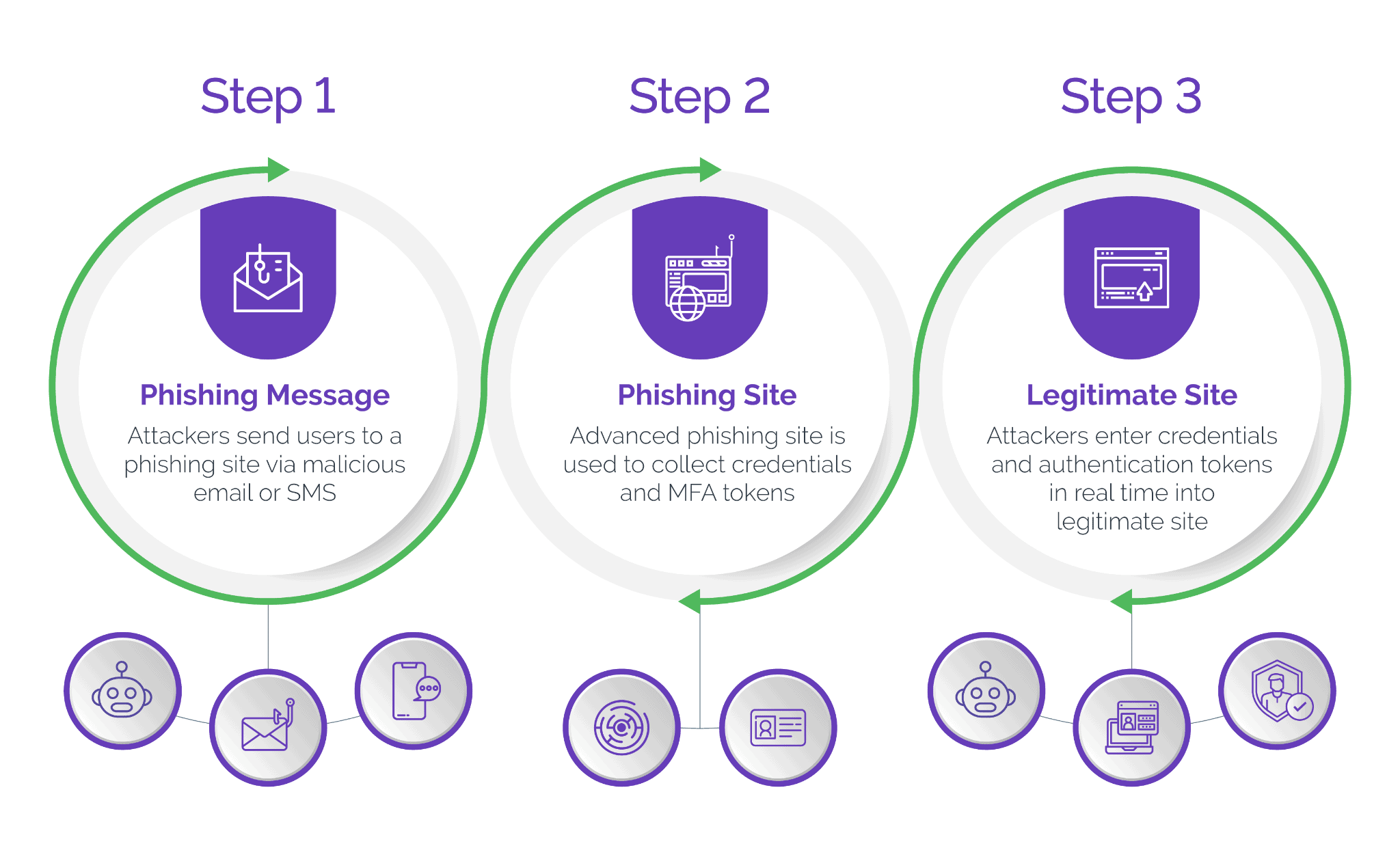
At its core, a MITM phishing site, also known as an adversary-in-the-middle, advanced phishing or reverse proxy site, serves as a mediator between a bank's internal servers and external consumers. Unlike traditional phishing, where attackers create deceptive websites to trick users into providing sensitive information, reverse proxy phishing introduces a more dynamic and elusive approach.
In this threat, cybercriminals leverage the man-in-the-middle mechanics as a way to intercept and manipulate user interactions with legitimate banking websites — all in real time.
In a typical scenario, attackers use publicly available information to craft meticulous, personalized emails or SMS messages that convincingly mimic the communication style and branding of legitimate businesses. These phony messages are becoming increasingly difficult to detect because cybercriminals are leveraging AI technologies to create perfectly worded communications. As unsuspecting consumers engage with these emails or texts, they are directed to advanced phishing sites that are nearly indistinguishable from legitimate sites.
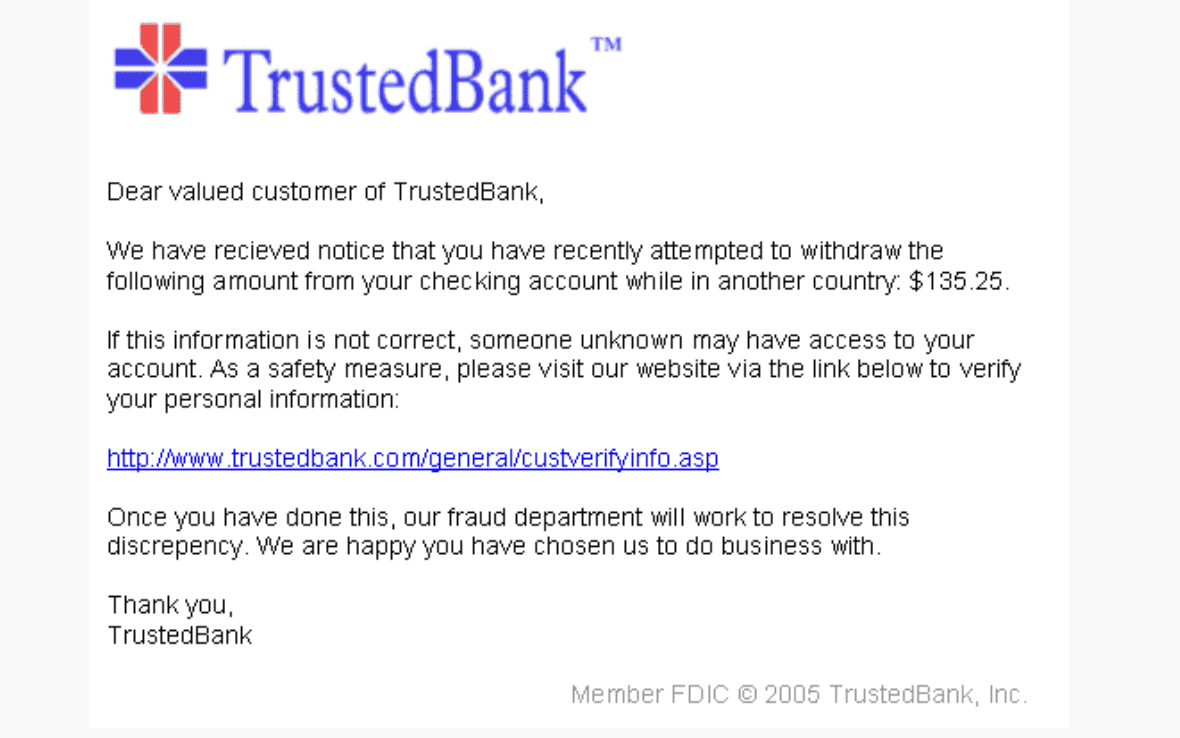
These phishing sites act as intermediary servers, reading the website source code in real time off the target bank’s website, intercepting the user's request before directing it to the legitimate banking website. This real-time interception provides threat actors with immediate access to the user's input, including login credentials and multi-factor authentication (MFA) codes. This level of sophistication and immediate access sets man-in-the-middle phishing apart from conventional phishing methods.
And because the deceptive element operates deep behind the scenes, it is challenging for both consumers and financial institutions to identify the malicious activities until it’s too late.
Advanced Phishing Turns Evil
A phishing-as-a-service (PaaS) platform named EvilProxy has emerged on hacking forums, offering a streamlined approach to stealing authentication tokens from various vendors, including Microsoft, Apple, Twitter, Facebook, Google and more. This phishing kit significantly lowers the cybercrime entry barrier, simplifying the execution of MITM phishing attacks.
EvilProxy goes beyond by providing instructional videos, a user-friendly graphical interface, and pre-designed templates for cloning phishing pages to pilfer credentials and authentication tokens. With its intuitive interface, threat actors can effortlessly set up and manage phishing campaigns, leading to potential unauthorized access to valuable banking accounts. This heightened risk includes financial fraud, reputation damage and an expanded pool of cybercriminals targeting the commercial banking sector.
This convenience comes at a cost, with EvilProxy pricing starting at $150 for 10 days, escalating to $400 for a month. Despite the expense, the potential rewards are substantial, creating opportunities for exploitation or resale to other malicious entities, such as ransomware gangs.
Arkose Phishing Protection Fights MITM Attacks
Arkose Phishing Protection, building on the robust bot detection technology of Arkose Bot Manager, is specifically crafted to identify and block man-in-the-middle phishing attempts in real time within the online commercial banking sector. The multi-layered detection integrates device, network and behavioral signals, offering a tailored and comprehensive defense against evolving threats.
- Detect advanced phishing attacks in real time
- Protect users and block credential theft
- Inhibit interception of MFA/2FA codes
- Prevent stolen session/authentication tokens
- Warn users with customized alerts
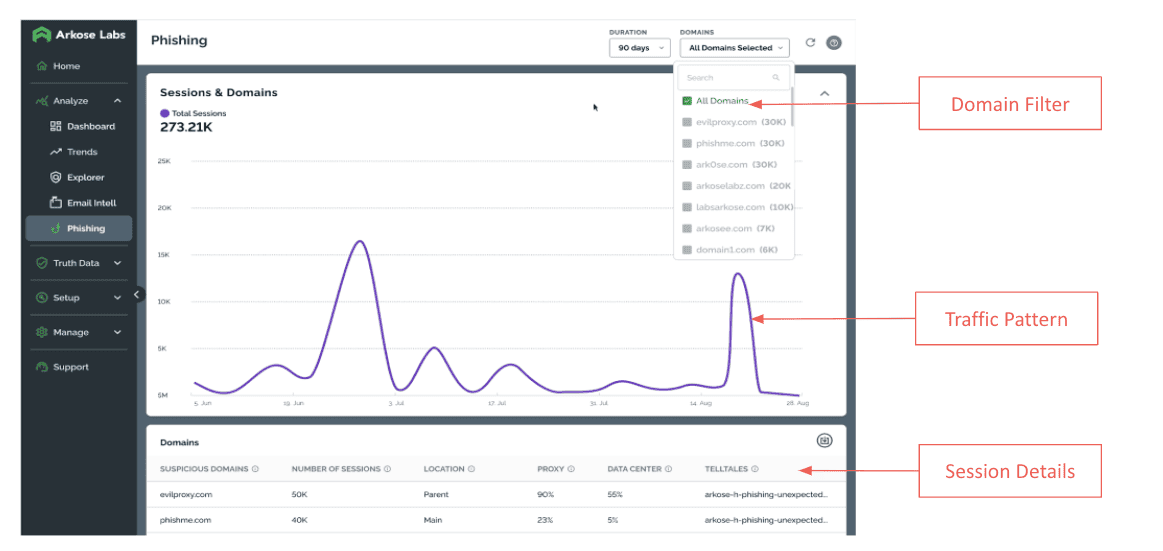
The Arkose Labs dashboard gives insight to the suspicious domains being used to target banking consumers and other end users:
Key capabilities tailored for the online commercial banking sector include:
- Real-time detection of advanced phishing attacks using client- and server-side signatures
- Managed phishing detection rulesets
- Hostname allow and deny lists
- Immediate end-user warning message
- Support for active interception and monitor-only modes
Understanding MITM phishing is crucial for protecting your bank and your consumers. By staying informed and proactive, you can strengthen your defenses and stay one step ahead of cyber threats. Learn more about how you can safeguard your business with Arkose Phishing Protection.