Data is possibly the most valuable asset on the internet today, and it certainly is for businesses. Data is what powers targeted advertising, customer engagement, and a host of other critical functions. As a result, organizations must work diligently to protect their data, mostly because the consequences of a data breach can be catastrophic. In addition to losing proprietary data, companies risk reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and legal penalties.
Data scraping is now a major problem for businesses of all sizes, as well as their customers. Understanding how scraping works and the techniques used by bad actors is imperative for businesses looking to protect their data and their customers. By implementing proactive measures and using the right tools, businesses can protect data from being scraped while also maintaining a strong competitive advantage and long-term cost savings.
What is data scraping?
Data scraping, or web scraping, is the process of extracting data from websites and other digital platforms, and is increasingly used by competitors, scammers, and cybercriminals to gain an unfair advantage or perpetrate different types of fraud. This type of data extraction involves the use of scripts or bad bots to collect data, often without the website owner's permission.
The data that is scraped can include text, images, videos, and other types of digital content. Data scraping can be useful for getting information from websites that do not have an API or for taking advantage of sites that do not allow access to their data through an API.
This type of data extraction engages in contact gathering for various purposes, including market research, data analysis, and content aggregation. It can be done manually, but it is usually done with software that automates the process. Google and other search engines use web scrapers to index websites and their content so that they can be searched.
Web scraping can also be used to collect data from social media sites, online marketplaces, and forums. However, it can also be used maliciously to steal valuable data, such as personal information, intellectual property, and trade secrets. As a result, businesses need to be aware of the risks associated with this type of data theft and take steps to protect themselves from this growing threat.
Main types of data scraping
Businesses face various types of data extraction, each with its own unique characteristics and potential risks:
Content scraping copies website content without permission, including text, images, videos, and other types of digital material. This type of scraping can include email addresses, phone numbers, and social media handles. This form of fraud is often used for email marketing, lead generation, and customer outreach. However, it can also be used for malicious purposes, such as identity theft, fraud, and spamming.
Businesses may also face the theft of personal data, where personal information such as names, addresses, and financial data is stolen from websites. This type of data scraping can result in a significant data breach, which can lead to reputational damage, regulatory fines, and legal action.
Website scraping uses the html code for the main article for web scraping. This language is designed for human end-users and not for ease of automated use. A scraper bot sends an http GET request to a specific website. The website responds and the scraper parses the html document for a specific pattern of data. Once the data is extracted, it is converted into whatever format the scraper bot’s author designed.
Javascript is a powerful and fast method for extracting text and links from html pages. It is also used to target a linear or nested html page. Website scraping involves the use of javascript to retrieve content from a web page and process it into a data file.
Price scraping involves a data gathering technique that extracts pricing information from various e-commerce websites. This technique is commonly used by competitors to gain a competitive edge by analyzing market trends and pricing strategies. Additionally, customers can also use price scraping tools to find the best deals and compare prices across different platforms.
Even so, businesses may face negative consequences from price scraping as it can lead to reduced revenue and profit margins. This is because price scraping allows competitors to easily monitor the pricing strategies of their rivals, leading to intense price competition. Further, the excessive use of price scraping can result in server overloads and other technical issues that can negatively impact website performance.
Screen scraping refers to the technique of extracting data from a visual output generated by a software application. This method involves using specialized software that can interpret the graphical interface of an application and extract the relevant data. Screen scraping software has become increasingly popular due to its ability to automate data extraction from a wide range of applications, including web browsers, desktop applications, and mobile apps.
With screen scraping tools, businesses can quickly and easily extract data from various sources, which can be used for analysis, reporting, and decision-making purposes. Additionally, screen scraping can help organizations to reduce manual data entry tasks and improve data accuracy by eliminating human errors. However, it is important to note that this form of extraction may raise legal and ethical concerns, particularly when it involves extracting data from third-party websites without permission.
The dark side of data scraping
Data scraping or web scraping is an essential tool for organizations to access and collect data from the internet—but it also has a dark side that poses serious risks to businesses and their customers. While data scraping is used for a variety of purposes, from market research to price monitoring to lead generation, it can also be used to commit all sorts of cybercrime, from identity theft, fraud, and other criminal activities. For example, scraped personal information can be used to create fake accounts, apply for loans or credit cards, or launch phishing attacks.
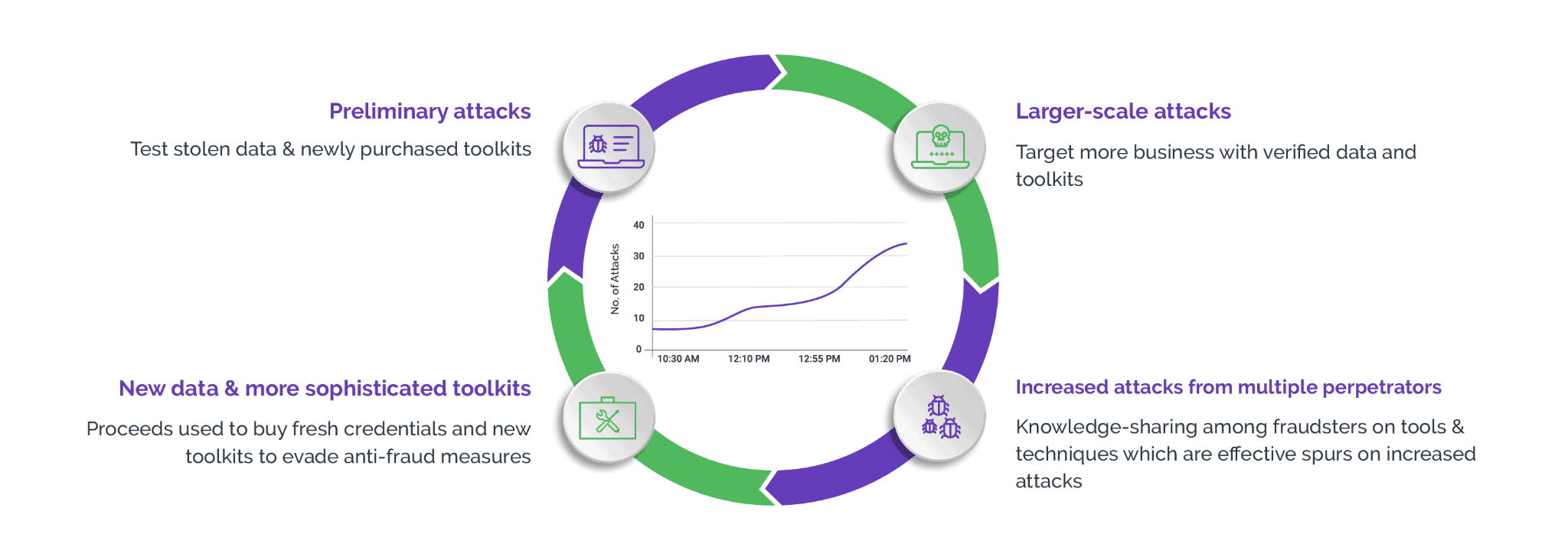
Scraped intellectual property, such as trade secrets and copyrighted materials, is often used to gain a competitive advantage or generate illicit profits. To make matters worse, scrapers can use advanced tools to access confidential data stored on company servers, giving them access to sensitive information such as financial records and client data.
Regulations such as the EU General Data Protection Regulation and the California Consumer Privacy Act provide organizations with guidance on how to properly access and use data from the internet. Additionally, organizations should ensure that any data scraped is used responsibly and does not violate any privacy laws.
How businesses can fight data scraping
To protect themselves, businesses should consider implementing several measures. Firstly, they can use website monitoring tools that detect scraping attempts in real-time and send alerts when suspicious activities are detected. These tools can help businesses identify the source of the scraping activity and take immediate steps to mitigate the damage.
Businesses can also limit the amount of publicly available data on their websites by using robots.txt files or implementing CAPTCHA-based mechanisms, like Arkose MatchKey, that verify the authenticity of the user. By reducing the amount of publicly available data, businesses can make it harder for data scrapers to collect valuable information.
Organizations can take legal action against data scrapers as well by using copyright laws, terms of service agreements, and other legal tools that protect their intellectual property. These defensive actions enable businesses to deter potential data scrapers and hold them accountable for any damages they cause.
Another approach businesses can take to protect themselves against data scraping is to work closely with their legal teams. By doing so, organizations of all sizes can better understand the legal implications of data scraping and develop effective anti-scraping strategies that are tailored to their specific needs. This can involve conducting regular audits of their data security protocols, identifying vulnerabilities, and developing contingency plans to respond to data breaches. Organizations can also collaborate with industry associations, cybersecurity experts, and law enforcement agencies to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices for data protection.
What’s next for data scraping?
Data scraping has come a long way and is continuing to evolve, with new techniques and technologies being developed all the time. There are now many data scraping tools available on the market. Some of these tools include Data Scraper (Chrome Plugin), Data Scraper Slots, and more. These tools allow users to extract data from human-readable output from another program.
As more businesses and industries move towards digital operations, data scraping will become increasingly important to help them stay ahead of the competition. In the near future, we can expect to see data scraping become even more automated, with AI and machine learning playing a greater role in how data is collected and analyzed. By leveraging these advanced technologies, businesses can gain deeper insights into their customer base, target new markets, and optimize their content for better search engine rankings. As data scraping technology continues to improve, it will become a key factor in helping businesses stay competitive and maximize their return on investment.
Data scraping is becoming more and more popular due to its ability to quickly and efficiently gather large amounts of data from a variety of sources. This data can then be used to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and competitor analysis. Also, data scraping can be used to automate tasks such as web crawling, price comparison, and content optimization. When leveraging the power of data scraping, businesses can gain a competitive advantage and stay ahead of the competition.
How does Arkose Labs prevent data scraping?
Arkose Labs provides businesses with a multi-layered defense against data and website scraping by using a combination of machine learning and human challenge-response technology. This enables the system to detect and stop automated tools, as well as manual efforts. It does this by analyzing the user's behavior and profile to determine if they are a legitimate user or a potential threat.
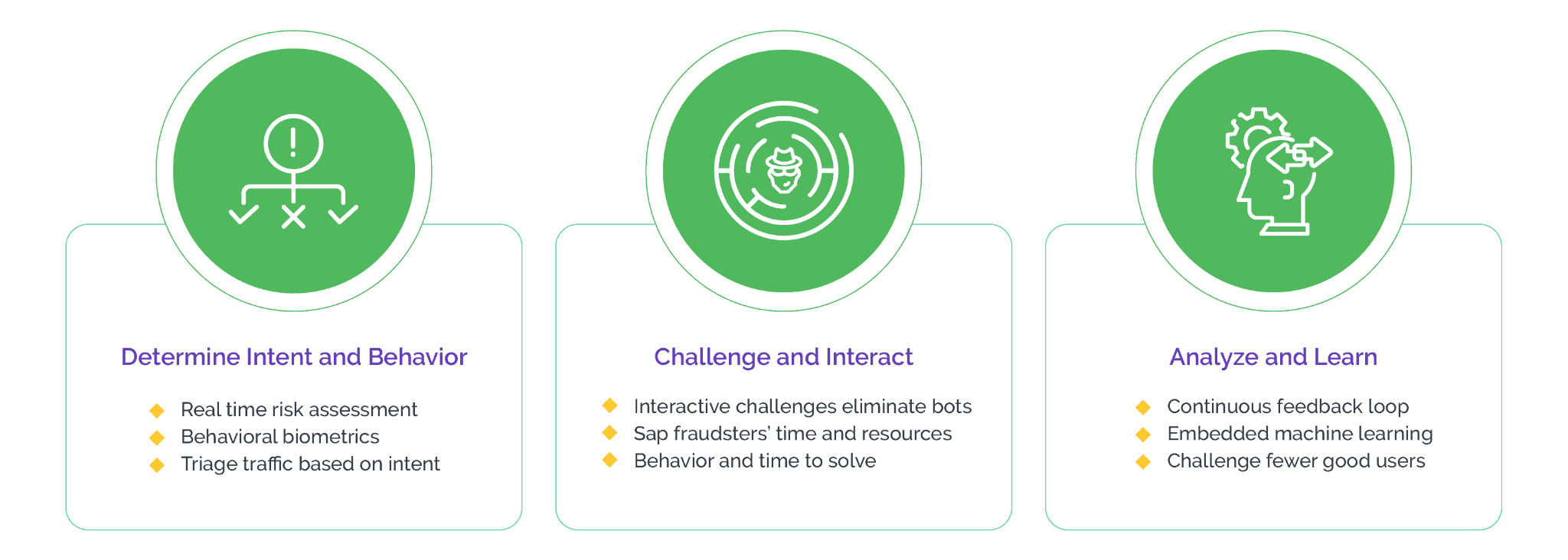
If a threat is detected, the system triggers the challenge-response process of Arkose MatchKey, which requires the user to answer a series of questions or solve a set of puzzles in order to gain access. This deterministic approach ensures that only legitimate users are able to access the business's data or website.
In fact, Arkose MatchKey is the strongest CAPTCHA in the industry. Bots, which can bypass traditional CAPTCHAs, cannot clear these challenges at scale as the 3D challenges are generated in real-time and are designed to counter the newest bot technology, making them resistant to automated solvers.
Arkose Labs' approach of eliminating the need to capture personally identifiable information except for the IP address not only alleviates privacy concerns, but also helps businesses maintain the trust of their customers. Additionally, clients of Arkose Labs benefit from ongoing managed services and actionable insights to stay ahead of the developments in bot technology and adapt to evolving threats.
To learn more about the Arkose Labs approach to data and web scraping, contact us anytime to book a demo.