What is Website Scraping?
Malicious scraping, or web harvesting, refers to bot-driven attacks that are aimed at extracting large volumes of data from websites and applications. This harvested data is then used to fuel criminal activities and fraud such as new fake account registration, account takeover, fake listings and reviews, inventory hoarding, and more. Apart from fueling numerous types of fraud, scraped data can be sold off to third parties or competitors.
We've heard the phrase "Data is the new oil" and certainly data is the main currency powering the digital economy. As more and more consumers use digital channels for shopping, banking, entertainment, and even socializing, there is a wealth of data for fraudsters to harvest. While businesses collect this data to improve their offerings, personalize customer experience, and upsell their products or services, malicious actors also look to steal information for financial gain.
Apart from consumer data, automated scraping tools are used to target commercially-valuable content, images and sensitive business data. Selling off scraped databases of verified customer information on the dark web or pricing details to competitors, or hoarding inventory of limited-edition items for resale later, are some of the easy money spinning options for fraudsters. Therefore, malicious scraping can lead to financial and reputational losses for businesses.
How Do Attackers Monetize Scraping?
Attackers are in the business of making money and automated scraping provides them with a low-investment method to harvest large volumes of data at scale. Some of the common ways attackers use to monetize scraping are as below:
-
Consumer data:
Data is essential to the success of digital businesses. When fraudsters disseminate stolen data-either for free or monetize it-businesses incur losses. Often, attackers sell the stolen databases to third parties or on the dark web to make money quickly. They also use the stolen data to improvise their attack strategies to launch more sophisticated and targeted attacks including account takeover, fake new account registration, and spam.
-
Business data:
Scraping of sensitive business data-such as pricing details-and selling them to competitors can lead to extirpating the marketing strategy of a business.
-
Web content:
For many businesses, content is their primary source of revenue. When this content is stolen, these businesses risk losing business viability and their existence is threatened.
-
Images:
Social media platforms have emerged as a haven for fraudsters. Using stolen data and images, they can create fake social media profiles and impersonate genuine users to request fund transfers from their network of friends. Fraudsters can even morph the pictures and use them to extort money from the users.
-
Denial of inventory:
Fraudsters can overwhelm business networks leading to denial of inventory attacks that disrupt business operations and cause losses.
-
Fake reviews:
Using stolen data, fraudsters can downvote products or write fake reviews to cause damage to the reputation of a business.
-
Spam:
Stolen email addresses allow fraudsters to disseminate spam and overwhelm users.
-
Phishing:
Databases of scraped user details are used as the building blocks for phishing campaigns that enable fraudsters to dupe unsuspecting users into making wire transfers or divulging confidential information.
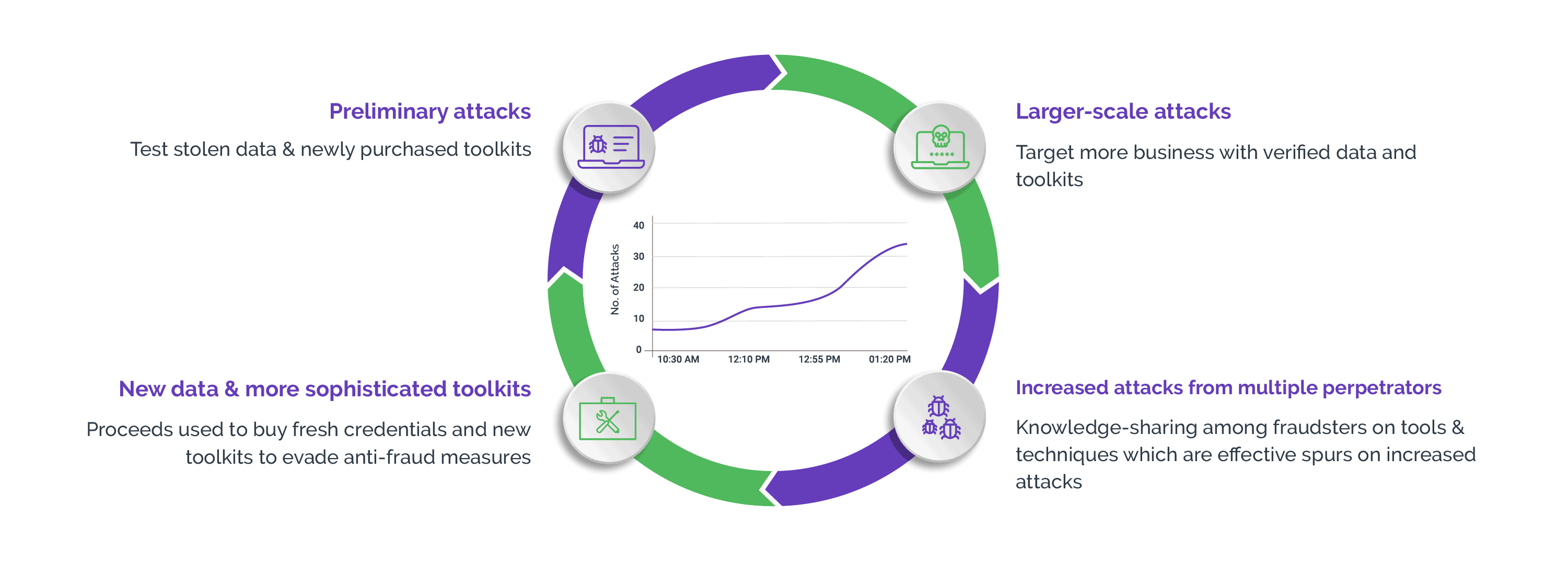
Why Must Businesses Address Website Scraping?
Scraping is a high-volume, low-monetization attack vector. Therefore, automation is used to achieve sufficient scale to drive return on investment. Theft of confidential consumer data also increases the risk of digital identities being compromised at scale. This is why automation using bots has resulted in scraping snowballing into a big challenge for today's digital businesses.
Many businesses create products and services on the basis of their customers' preferences. They gain these insights by analyzing the customer data, which may include content and images. This, in effect, means that customer data helps these businesses generate revenues. When attackers exploit this data, the commercial viability of the business model is put to risk and the existence of the business itself is threatened.
Further, directives such as the GDPR mandate businesses to prioritize security of customer data. Inability to protect consumer data due to unauthorized scraping can make digital businesses non-compliant with the directive and attract hefty penalties. This also leads to an erosion of customer trust.
It is worth remembering that not all scraping is for malicious purposes. For instance, individuals such as journalists, researchers, and even students use information, statistics, and anecdotes available in the public domain for their notes or theses. Certain businesses scrape publicly available data for analytics or to offer data as a service-such as a niche news aggregator. Further, search engines crawl the websites and index them for search results.
However, when businesses do not know how to protect against bot-driven malicious scraping attempts, they increase their vulnerability and face a heightened risk of data exposure. It is, therefore, of utmost importance for digital businesses to proactively identify and stop automated scraping attempts.
Limitations of Traditional Approaches
The first step for digital businesses to protect against bot-powered scraping attempts is to remain vigilant and deploy solutions that can stop scraping attempts right at the entry gates. However, legacy defense mechanisms cannot provide the level of protection that businesses need in an ever-changing threat landscape.
There are bot-mitigation solutions that are available for free or cheaply. However, such solutions ultimately cost businesses in many ways. In addition to customer churn, businesses risk damage to consumer trust and brand image that are long-term and often irreparable. For instance, CAPTCHAs were designed specifically to protect digital businesses from the onslaught of bot-driven attacks such as scraping. However, while bots have evolved at a great speed, CAPTCHAs have failed to keep pace. This has led to legacy CAPTCHAs being outsmarted by even the basic bots.
As well as bypassing traditional solutions, bots are now advanced enough to mimic human behavior with a certain level of accuracy. They are programmed in such a manner that in an event a more nuanced human interaction is required than what they can handle, they hand over the attack baton to human sweatshops. This makes it all the more challenging for businesses to thwart complex, automated scraping attempts.
A Layered Approach to Protecting Against Scraping
Digital businesses need a cost-efficient, long-term solution that goes beyond mitigation and adapts to the evolving bot threats. They must adopt an integrated approach that can empower them to fight the onslaught of automated attacks with confidence and is cost-effective in the long run.
The Arkose Labs platform enables businesses to do just this by leveraging continuous intelligence to uncover the true intent of each user and combining this real-time risk assessment with adaptive enforcement challenges for superior bot identification.
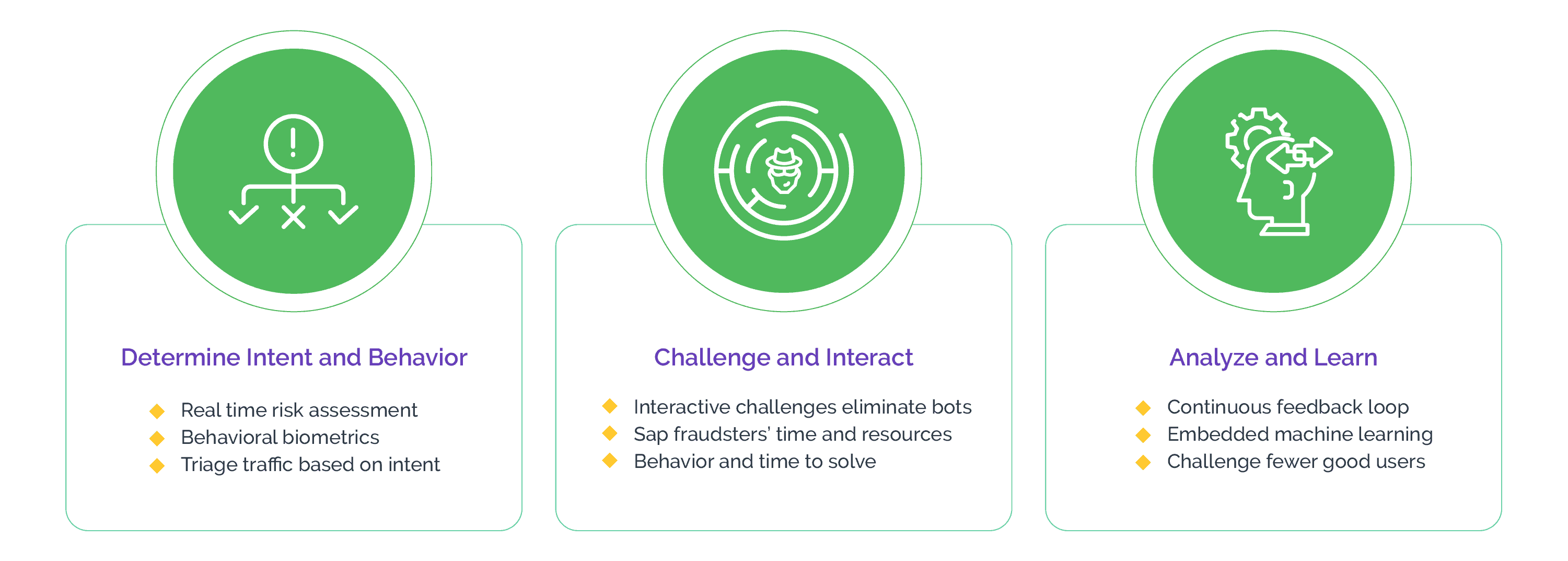
Based on the risk assessment, a user may be presented with one of our custom 3D challenges. This is particularly useful in rooting out scripted attacks and trained bots. Good users, if presented with a challenge, find no difficulty clearing them, thus preserving user experience for the genuine users. When bots-that can easily bypass CAPTCHAs-try to clear these challenges at scale, however, they fail instantly. This is because the 3D challenges are rendered in real-time and are specifically trained against even the most leading-edge innovations in bot technology, which makes them resilient to automatic solvers.
Arkose Labs takes this approach because it eliminates the need to capture any personally identifiable information of the users except for the IP address. It also alleviates privacy concerns and allows businesses to continue enjoying the trust of their customers. Further, Arkose Labs' clients benefit from ongoing managed services as well as actionable insights to adapt to the evolving threats and stay ahead of the developments in bot technology.
Arkose Labs is highly effective at protecting against unwanted scraping activity targeting:

To learn more about the Arkose Labs approach to bankrupting the business model of fraud and book a demo, click here.