Social media platforms are a goldmine of personal information. Not only are they home to billions of user accounts – roughly 4.9 billion individuals are active on social media worldwide today1 – but they are packed with details like usernames, email addresses, phone numbers, organization names, photos, and so on. These accounts are ripe for plucking by bad actors.
Automated social media scraping is a quick and dirty way for attackers to harvest all this data at scale and speed, with minimum investment. A combination of open accessibility, unprotected APIs, easily structured HTML, insufficient anti-scraping measures, and more contributes to the ease of website scraping.
Stopping the bots and human attackers requires robust security measures, proactive monitoring, and a future-ready approach that not only fights online abuse today, but also prepares social media platforms to crush evolving attack tactics in the future.
Businesses lose revenue and customer trust
Data is at the core of the commercial viability of any business today. When this data is stolen, exploited, or manipulated, businesses risk significant financial losses as well as a deficit in customer trust. For social media sites especially, website scraping can be highly detrimental:
- Data Privacy Breaches: Web scrapers extract user data, including personal information, posts, and messages, which can lead to significant data privacy breaches and violate user trust.
- Content Misuse: Scraped content is misused for spamming, phishing, or spreading misinformation, tarnishing the platform's reputation and potentially harming users.
- Loss of User Engagement: When scraped content is used elsewhere without proper attribution, it can result in reduced audience engagement and activity on the social media channel.
- Revenue Loss: Scraped data is often used to create fake accounts or profiles, impacting the accuracy of user metrics and ad targeting, generating potential revenue loss.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Social media platforms must comply with various data protection and privacy laws. If scraped data contains personal information and is misused, the platform may face legal consequences and damage its reputation.
- Network Overload: High-volume scraping puts a strain on the platform's servers, causing performance issues, slowdowns, or crashes, and negatively affecting user experience.
- Intellectual Property Violation: Social media scrapers may steal copyrighted content, leading to intellectual property violations and potential legal actions.
Distinguishing malicious from authentic traffic can be challenging
Clearly, website scraping poses significant threats to social media platforms' integrity, user privacy, revenue streams, and legal compliance. But it isn’t always easy to tell the attackers from the legitimate site users.
A case in point is one of our customers, a popular social networking giant with more than 600 million global users. The social networking platform was facing hot pursuit from attackers, who were looking to scrape user information so they could abuse it for financial gain.
The scale of operations and popularity of the platform meant that automated scraping would have resulted in large-scale financial losses for the organization and downstream fraud, originating from the stolen data, for authentic users. The social media platform was facing an uphill task trying to filter out malicious traffic from authentic users, as it sought to ensure continued revenue generation and protection for its genuine users.
Part of the reason the platform struggled to identify automated traffic is because of the sophisticated nature of advanced bots. These bots, which closely mimic human behavior, are scripted in such a way that they can circumvent traditional bot detection solutions like legacy CAPTCHAs. They use dynamic IP addresses and continuously adapt their tactics, and the presence of human-assisted attacks and shared network IP addresses further blurs the lines. In addition, the overlapping characteristics displayed by legitimate users complicates the task of defining clear patterns for bot detection.
Preserve social media user experience and revenues
For all around protection of their platforms and customer interests, social media businesses need a fresh approach to tackling online abuse. The solution must go beyond traditional defense mechanisms, using continuous intelligence and analyzing hundreds of parameters to create attack telltales. Instead of outrightly blocking risky users, it should use targeted friction to pin down malicious users without disrupting the digital journeys of authentic customers.
One example of how this can work is seen with our aforementioned customer, the social networking giant. They deployed the Arkose Labs Bot Manager solution to detect and filter out risky users with certainty. The platform uses multi-layered detection that aggregates real-time signals to identify risky users and then presents them with targeted friction in the form of Arkose MatchKey challenges.
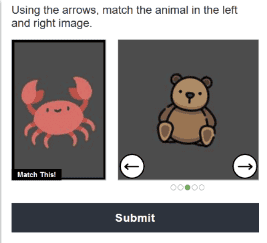
In most cases, the social media platform’s authentic users did not even see the Arkose MatchKey challenge, and those that did cleared the challenges with no difficulty at all. This meant there was no disruption to the user experience for authentic users. Potentially suspicious users – such as those that viewed multiple user profiles in a session, without logging in as a recognized user – were presented with an Arkose MatchKey enforcement challenge. Automated scripts and bots trying to clear these context-based challenges at scale failed instantly, as our proprietary challenges are tested and hardened against the most advanced AI and machine learning technology and automation.
In addition, there was a marked uplift in good user throughput and a remarkable reduction in automated scraping requests. With its multiple advantages, the Arkose Labs solution not only helped the social media platform save millions of dollars but also protected its sanctity and improved the user experience for authentic users.
At Arkose Labs, we guarantee a 100% SLA guarantee to all our customers against automated attacks. To learn how we helped the social networking platform root out automated scraping attempts with certainty, read the case study or contact us for a demo.