Types of fintech fraud
What are the types of fintech fraud?
![]()
Driven by the use of technology, fintech fraud continues to evolve. Some common types of fintech fraud include:
Account Takeover / Credential Stuffing
Using stolen credentials or exploiting weaknesses in security measures to gain unauthorized access to a user’s financial account.
Phishing / Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Using deceptive emails, texts or fake websites to trick individuals into sharing sensitive information like login credentials or financial details.
Payment Fraud
Making fraudulent transactions with stolen credit card information, mobile payment apps or cryptocurrency wallets.
Loan / Mortgage Fraud
Opening new lines of credit through fraudulent loan applications or misrepresentation of financial information, which ultimately damages the credit scores of the victims.
ACH Fraud
Exploiting vulnerabilities in payment systems or using stolen account information to misappropriate funds from financial accounts by unauthorized transactions or alterations made through the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network.
Robo-Adviser Fraud
Executing fraudulent trades or misappropriating funds by manipulating automated investment platforms or algorithms.
Investment Scams
Targeting unsuspecting users with promises of guaranteed profits, high returns with little to no risk, or insider information through fraudulent schemes.
Advance Fee Fraud
Tricking users into paying upfront fees to receive a promised benefit, such as a loan, inheritance or prize that is never delivered.
Insurance Fraud
Falsifying insurance claims or misleading insurance companies into obtaining payouts the fraudsters are not entitled to.
Credit Card Fraud
Making purchases or withdrawing cash, often through unauthorized use of stolen credit card information or card-not-present (CNP) transactions.

What are the popular methods of executing fintech fraud?
Phishing Attacks: Fraudsters use deceptive emails, texts or fake websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information like login credentials or financial details.
Generative AI: Attackers enhance phishing attempts using AI to make fraudulent communications appear more legitimate.
Malware: Malicious software is deployed to compromise devices or networks, granting unauthorized access to financial accounts or stealing personal information.
Social Engineering: Impersonation of trusted entities (e.g., financial institutions) to manipulate users into divulging sensitive information or performing compromising actions.
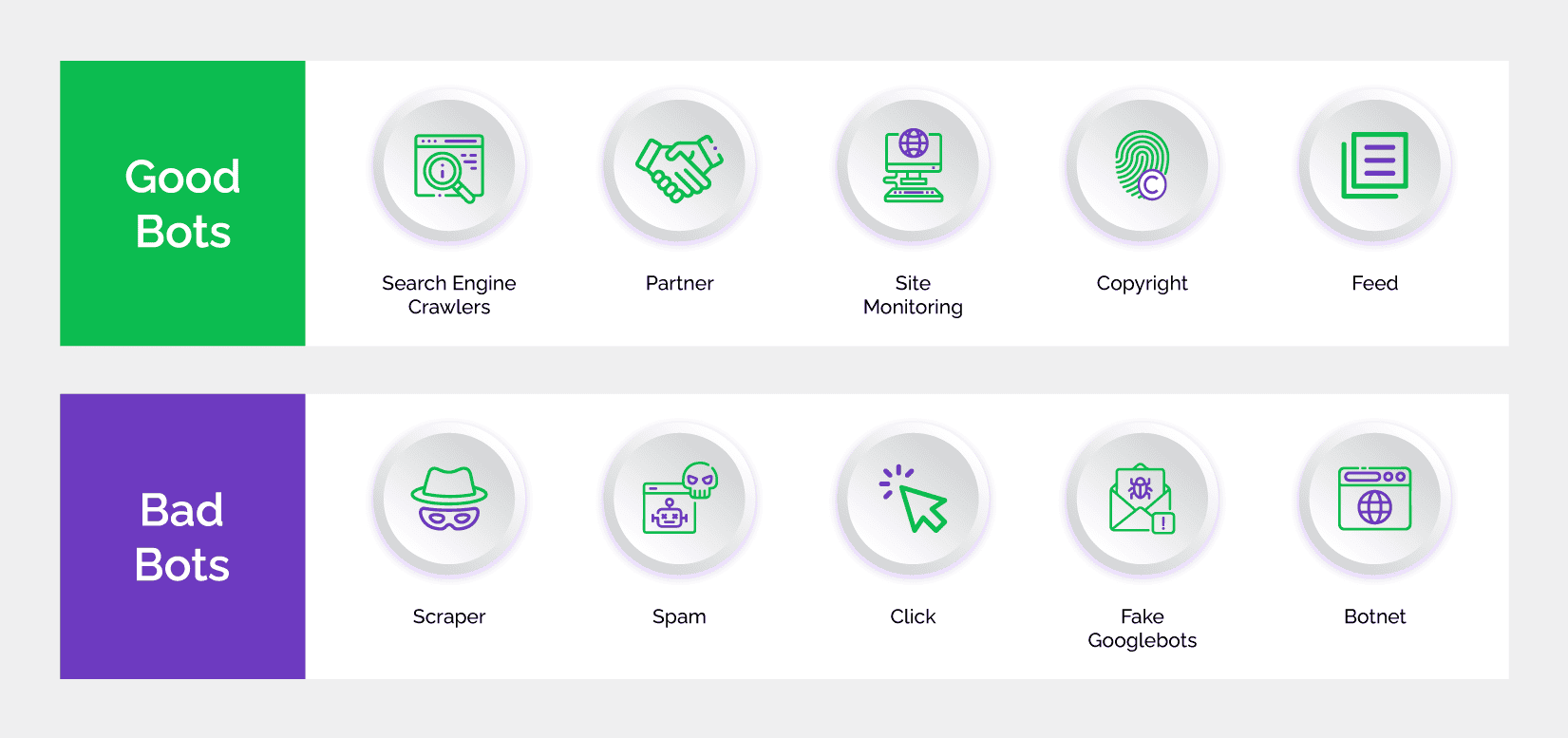
How do bots contribute to fintech fraud?
- Automated Execution: Bots are used extensively to automate phishing, account takeover and other fraud activities, allowing attackers to scale their efforts. Learn more about the risks and prevention strategies for automated bot attacks.
- Phishing Campaigns: Bots send out large volumes of phishing messages, increasing the likelihood of fraud. Discover more about bot mitigation.
- Exploiting API Vulnerabilities: Attackers use bots to exploit weak APIs, leading to unauthorized access. Learn more about API security.
- Human-like Behavior: Modern bots mimic human actions, making them harder to detect. Learn all you need to know about fraud detection.
- Overwhelming Traffic: The sheer volume of bot traffic can overwhelm networks, complicating fraud prevention. Learn about the impact of bot traffic.
- Facilitating Account Takeovers: Bots can also facilitate account takeover attacks by automating credential stuffing. Understand more about the risks of account takeover.
What are the consequences of fintech fraud on businesses?
- Monetary Losses: Fintech fraud leads to substantial financial losses, especially for start-ups lacking robust defense mechanisms.
- Impact on Start-ups: Fraud can undermine the viability of fintech start-ups, making it difficult to attract investment, scale operations, or develop new products.
- Loss of Brand Equity: Fraud incidents can erode trust among customers, investors, and stakeholders, leading to lost business opportunities and revenue.
- Legal and Regulatory Risks: Businesses may face fines, legal action, or license cancellations due to failures in ensuring customer security and data protection, damaging confidence in the fintech ecosystem.
Why is it urgent to combat fintech fraud?
There is an urgent need for fintech fraud prevention as it continues to grow on the back of technological advancements, causing colossal damage to consumers, businesses and financial systems. Increasing digitization of financial services and the growing sophistication of fraud tactics is making it harder for anti-fraud teams to address the issue effectively. Unchecked growth of fintech fraud will not only cause increasing financial and reputational losses for individual businesses but also disrupt the integrity and sustainability of the financial services ecosystem.
It is therefore critical that companies take proactive measures toward fintech fraud prevention by implementing robust cybersecurity measures, collaborating with peers and fintech industry stakeholders, and promoting greater awareness and education about fraud prevention.
What are the signs of a potential fintech fraud attempt?
For effective fintech fraud detection, businesses must remain vigilant and monitor certain indicators of a potential fintech fraud attempt. Some telltales include:
- Unexpected account activity
- Unrecognized transactions
- Changes to account information,
- Irregularities in investment returns
- Unusual requests for upfront payments or fees
- Suspicious communications from purported financial institutions
- Phishing emails or messages requesting sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details
How to prevent fintech fraud?
Businesses must adopt effective strategies and take active measures to combat fintech fraud. A holistic and proactive approach to fintech fraud prevention can help strengthen the resilience of digital financial systems and protect against evolving financial fraud tactics. This may involve adopting a multi-layered approach that combines advanced technologies – such as AI, machine learning and blockchain – robust system security protocols and proactive risk management practices.
Implementing sophisticated fintech fraud detection software that leverages artificial intelligence and advanced machine learning algorithms can be useful in identifying suspicious patterns and anomalies in real time, enabling businesses to intervene swiftly and mitigate potential losses. Strong authentication measures, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric verification, can enhance the security of online financial transactions and reduce the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
Facilitating threat intelligence sharing and enabling coordinated responses to emerging fraud trends through collaboration and information sharing among financial institutions, regulatory agencies and law enforcement authorities can help implement robust fraud prevention measures. Additionally, businesses must conduct cybersecurity awareness and education programs for employees and customers to raise awareness about common fintech fraud tactics and how to recognize and report suspicious activities effectively.
A list of strategies that business can consider implementing is as below:
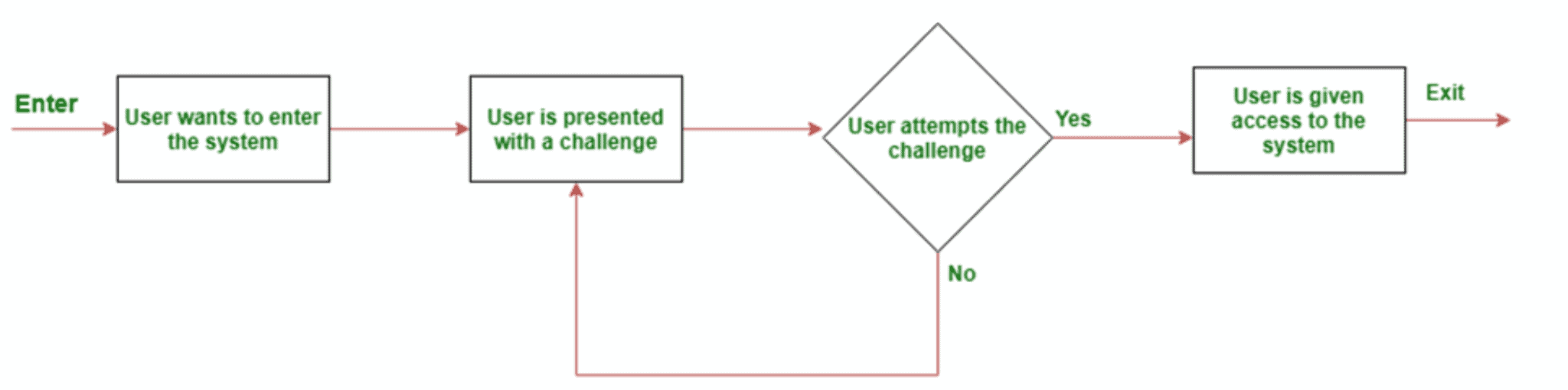
- Bot Detection and Mitigation: Utilizing a combination of behavioral analysis, machine learning algorithms and challenge-response mechanisms to identify and neutralize automated threats.
- Advanced Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, challenge-response authentication and device intelligence to enhance system security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Fraud Detection Systems: Deploying sophisticated algorithms and AI-powered tools to detect anomalies, suspicious patterns and fraudulent activities in real-time.
- Encryption and Data Protection: Using robust encryption protocols and secure data storage practices to protect sensitive financial, business and biometric data from unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Transaction Monitoring: Implementing real-time monitoring systems and automated alerts to detect unusual behavior, such as large or unusual fund transfers, and stop fraudulent activities promptly.
- Transaction Limits and Controls: Restricting high-risk transactions and preventing fraudulent behavior by setting transaction limits, monitoring account activity, and implementing access controls.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Conducting risk assessments regularly for fintech fraud mitigation by identifying vulnerabilities and implementing proactive measures.
- Compliance and Regulation: Adhering to regulatory requirements, such as KYC and AML compliance and implementing best practices to ensure data protection, fraud prevention, and customer authentication.
- Customer Education: Conducting awareness programs and educational resources to help consumers recognize common fraud tactics and phishing scams, and exercise security best practices.
- Collaboration: Sharing threat intelligence and coordinating responses to emerging fraud threats partnerships with fintech industry peers, regulatory agencies, and law enforcement authorities.
Want to know more about strategies and techniques to protect your enterprise from fintech fraud? Visit our finance and fintech solutions page.