Fraudsters are increasingly engaging in online banking fraud. They use deceptive tactics like phishing, malware, and social engineering to dupe users into sharing sensitive personal and financial information that is then used for several criminal activities.
Understanding Online Banking Fraud
Online banking fraud is any illicit activity on digital banking channels that uses consumers’ stolen personal information such as social security numbers, credit card information and phone numbers. It covers a range of deceptive practices, including online bank account takeover, stealing funds from the compromised accounts, fraudulent transactions, exploiting loyalty programs, money laundering, and identity theft.
These types of fraud can cause massive financial losses to consumers and banks through multifaceted threats to online banking systems.
Common Types of Online Banking Fraud
Common types of online banking fraud include:
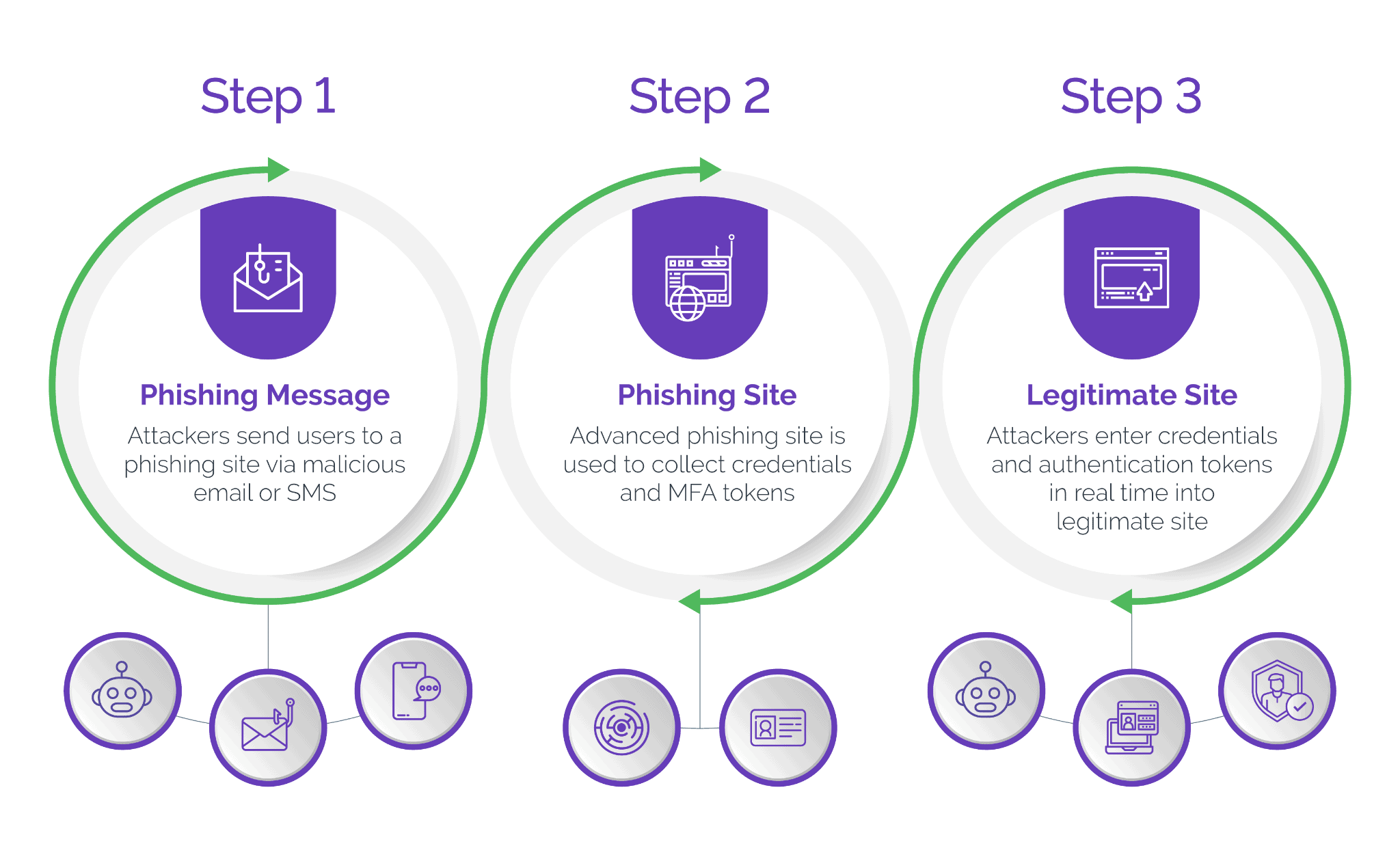
- Phishing: Tricking users into revealing sensitive information like usernames and passwords through fraudulent websites or emails
- Social Engineering: Impersonating individuals or entities to manipulate consumers into disclosing sensitive information or performing actions that profit fraudsters
- Malware: Infecting users’ devices to steal account credentials, manipulate transactions, or compromise account security using malicious software
- Account Takeover: Using stolen credentials or exploiting technical vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to checking accounts and make fraudulent transactions.
- Identity Theft: Stealing consumers’ personal information and abusing it to open fake new accounts, apply for loans, or conduct criminal financial activities without the user’s knowledge.
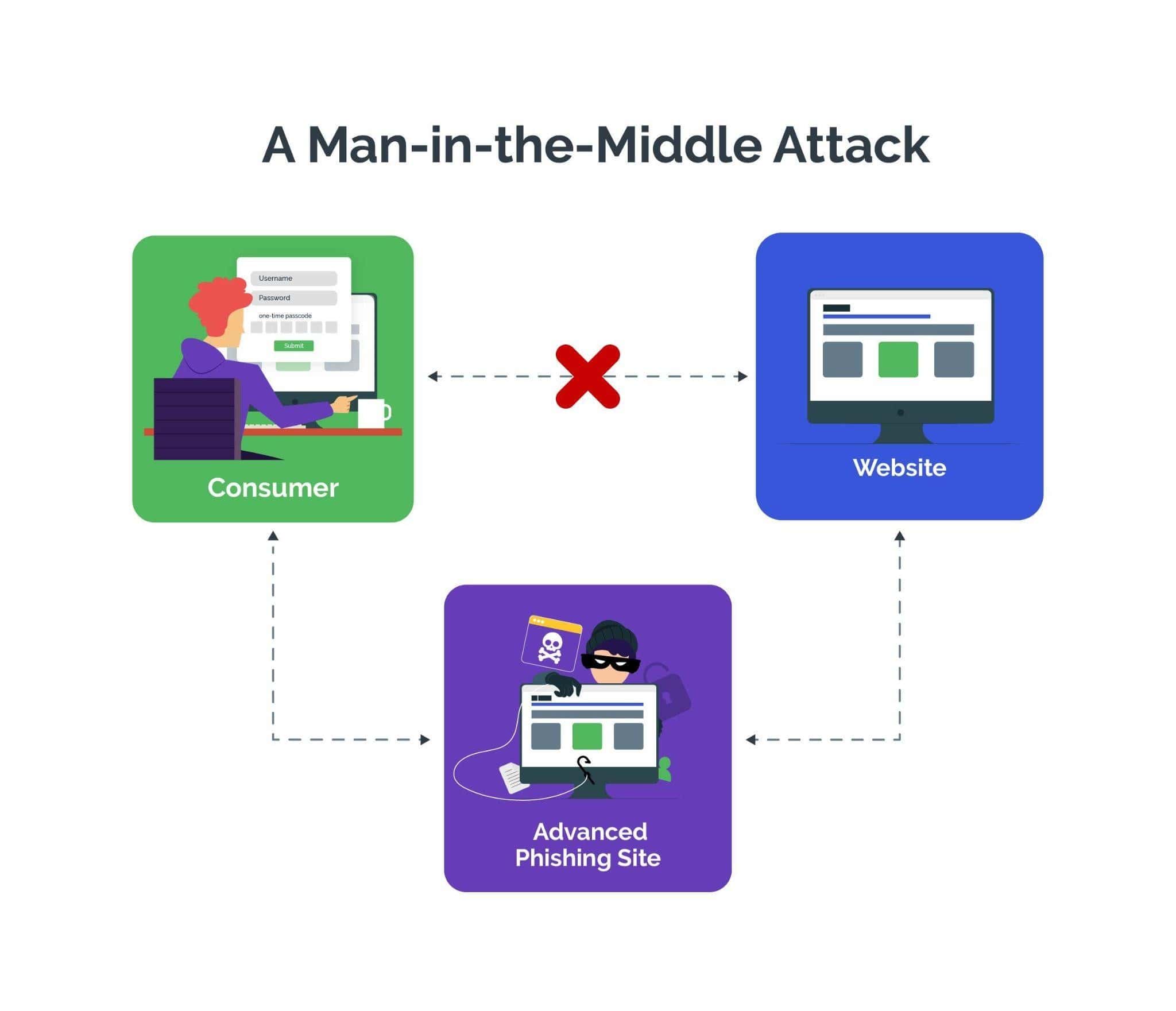
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Intercepting communication between genuine users and official websites to steal login credentials and gain access to accounts.
- Card Skimming: Installing devices on ATMs or point-of-sale terminals to capture card information and make unauthorized transactions
- Insider Fraud: Employees or persons with internal access misusing their privileges for criminal activities such as unauthorized fund transfers or data theft
Technological Tools in Fraud Detection
To fight online banking fraud, financial institutions must use tools that leverage the latest technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, behavioral biometrics, and device fingerprinting, among others.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning analyze large volumes of transactional data in real time to help detect anomalies, suspicious patterns or fraudulent activities within financial transactions, enabling banks to proactively detect and respond to threats as they occur.
Behavioral Analytics for Fraud Prevention
By monitoring and analyzing users' behavior patterns, such as transaction history, login times and mobile device usage, behavioral analytics helps banks detect suspicious activities indicative of potential fraud.
The Role of Bots in Online Banking Fraud
In recent years, bots have come to play a significant role in online banking fraud.
How Bots Facilitate Fraudulent Activities
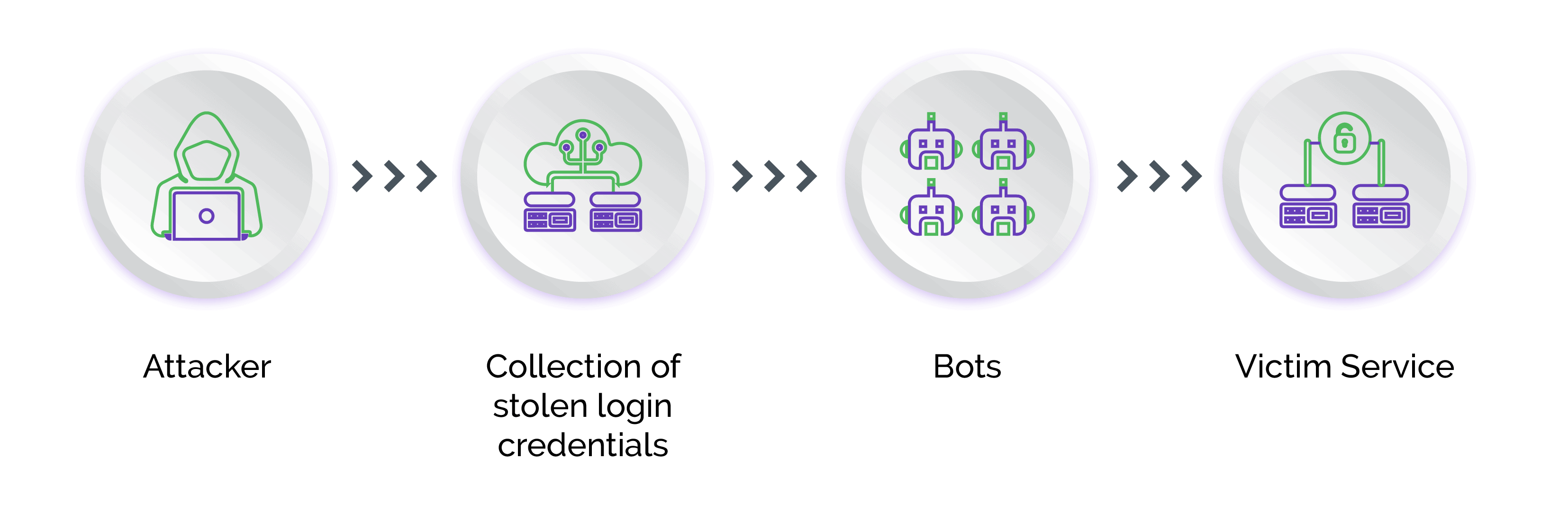
By automating various fraudulent activities, bots enable scammers to scale up operations, exploit vulnerabilities in banking systems and bypass security measures, making it harder for security teams to fight online banking fraud.
Bots can streamline and scale online banking fraud activities through automated distribution of phishing emails or messages, automated social engineering conversations through chatbots or messaging platforms to elicit users’ personal information, credential stuffing to test large volumes of username and password combinations, account takeover, new account and sign-up fraud, brute-force attacks, executing automated fraudulent transactions at high speed, exploiting vulnerabilities in online and mobile banking systems, and bypassing security measures to evade detection.
Detecting and Mitigating Bot-Driven Fraud
For effective bot protection, banks must implement sophisticated security measures such as device fingerprinting, behavior analysis, and smart challenge-response authentication, like Arkose MatchKey, to identify and block suspicious internet activity.
Banks must also prioritize continuous monitoring of transaction patterns, anomaly detection algorithms, and machine learning techniques to proactively identify and respond to automated bot attacks.
Implementing Strong Authentication Measures
Implementing strong authentication measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or biometric verification can help banks enhance user security.
Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of authentication that can mitigate the risk of online banking fraud. It requires multiple forms of identity verification, which helps reduce the risk of unauthorized access and account takeover even if fraudsters have access to users’ passwords.
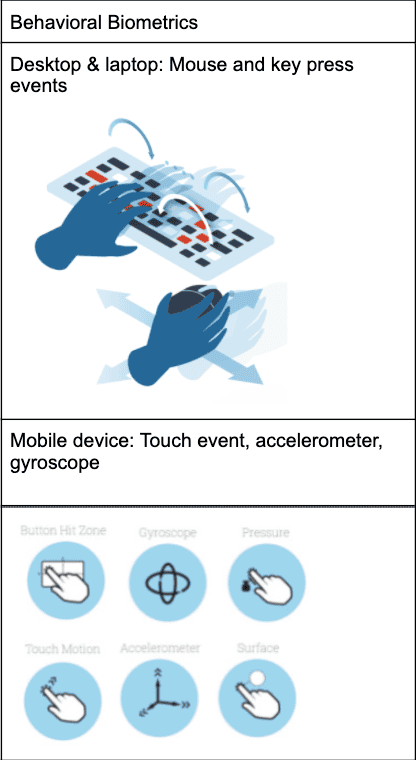
Biometric Verification Technologies
Biometric verification is a reliable and user-friendly method to authenticate customers using unique physical or behavioral characteristics, such as facial features, fingerprints, or voice patterns.
Educating Consumers on Fraud Prevention
Educating consumers on recognizing and responding effectively to potential threats can help fraud prevention efforts.
Creating Awareness About Phishing Scams
By raising awareness about common scams and best practices for safeguarding personal and financial information, financial institutions can help consumers protect themselves from becoming a victim of fraud.
Guidelines for Safe Online Banking Practices
Banks must create awareness about the importance of using a secure internet connection to prevent advanced phishing attacks for interception of sensitive information over public Wi-Fi. Additionally, banks must encourage users to regularly monitor their bank statements for any suspicious account activity or unauthorized transactions, keep login information confidential, and be cautious of phishing attempts through unsolicited emails or messages requesting personal information.
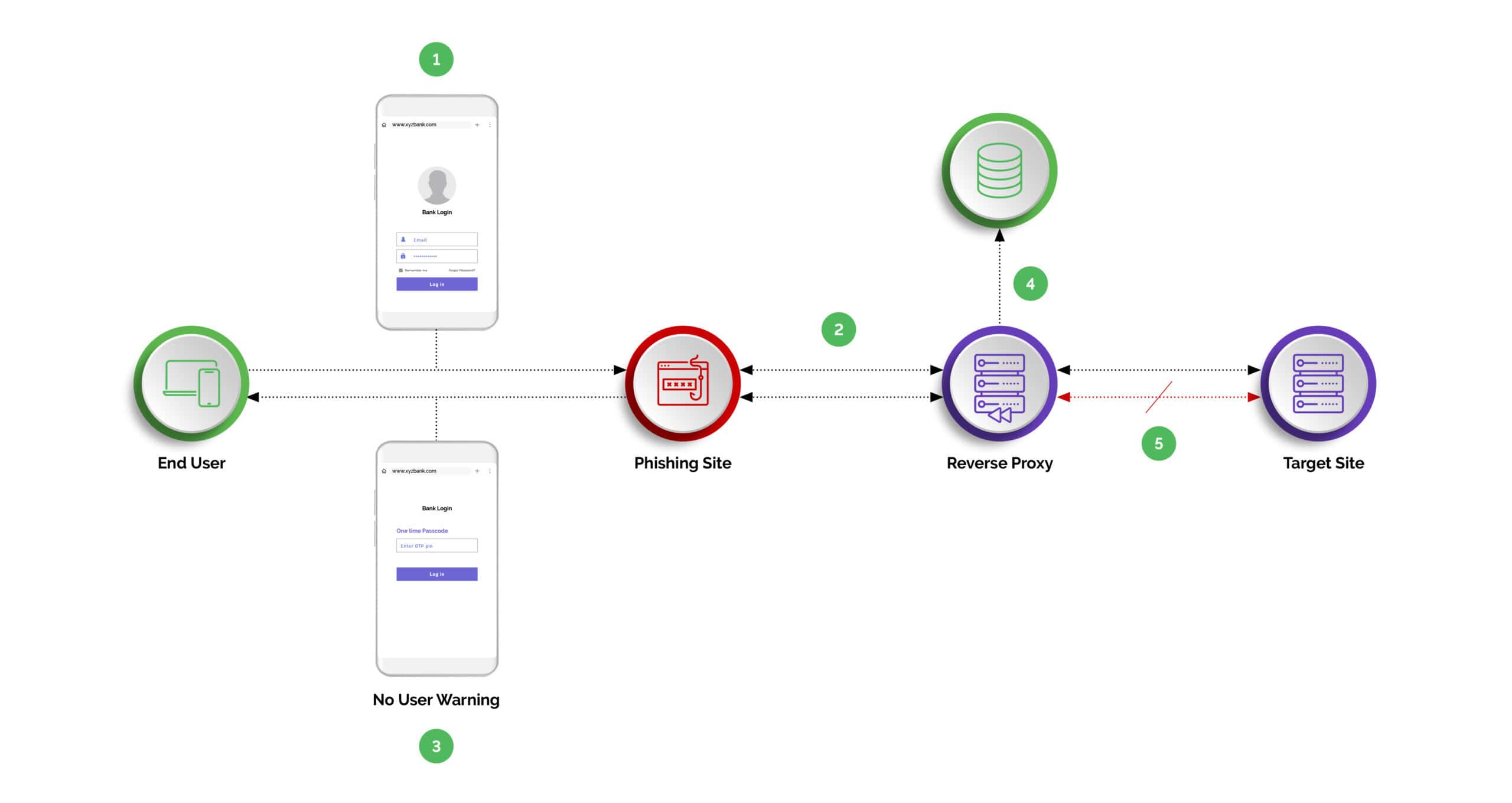
Regulatory Compliance and Fraud Prevention
Being a part of a highly regulated industry, banks and other financial institutions must adhere to data privacy and customer security regulations.
Adhering to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Laws
It is mandatory for banks to adhere to anti-money laundering (AML) laws to detect and prevent bank fraud and other illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing.
Complying with AML regulations allows banks to avoid legal consequences and reputational damage, while contributing to the overall integrity and stability of the financial system by fighting various types of online banking fraud.
Data Protection Regulations and Customer Privacy
Banks are also obliged to abide by data protection regulations and safeguard customer privacy, enabling them to mitigate the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and ensuring security of consumers’ financial accounts.
Real-World Case Studies of Detected Fraud
Online banking fraud is a growing challenge, as often it is detected after the damage is done. For instance, the Carbanak cybercrime group targeted more than 100 financial institutions globally, using malware to compromise banking systems, gain access to account information, and conduct fraudulent transactions, causing losses over $300 million.
Another case in point is of a massive online banking fraud by the cybercriminal group Lazarus targeting Bangladesh Central Bank. Cybercriminals used sophisticated hacking techniques to infiltrate the bank's network, trying to transfer around $1 billion from its account held at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Although most transactions were blocked, the group successfully managed to transfer around $81 million before detection.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
The above case studies highlight the importance of detecting and preventing sophisticated online banking fraud schemes to prevent immense financial and reputational losses. These incidents also underscore the criticality of strengthening defenses against evolving cyberattacks by implementing robust cybersecurity measures, employee training, collaboration, and information sharing among financial institutions and law enforcement agencies.
Recovery Processes After a Fraud Incident
After an incident, the bank must promptly inform affected customers and provide guidance on securing their online accounts to mitigate potential losses. Banks must thoroughly investigate the incident, enhance security measures, and make efforts to restore trust and confidence among customers.
Conclusion
Online banking fraud poses a significant challenge to banks and their customers. Cybercriminals continue to evolve their tactics and are increasingly leveraging easily and cheaply available bots to exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems.
To effectively fight online banking fraud, banks must implement robust security measures, comply with regulatory requirements, and collaborate with stakeholders. Additionally, banks must prioritize customer education and remain up-to-date with the evolving fraud trends to create a secure and trustworthy financial ecosystem.
Discover how Arkose Labs empowers banks, fintechs, and other financial institutions to fight online banking fraud.