What is an adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) attack?
An adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) attack, also known as a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, is a type of cyberattack where cybercriminals intercept, relay or alter the communication between two parties without their knowledge, while giving the impression of a direct communication. This can lead to data theft, identity theft, financial theft or other exploitations.
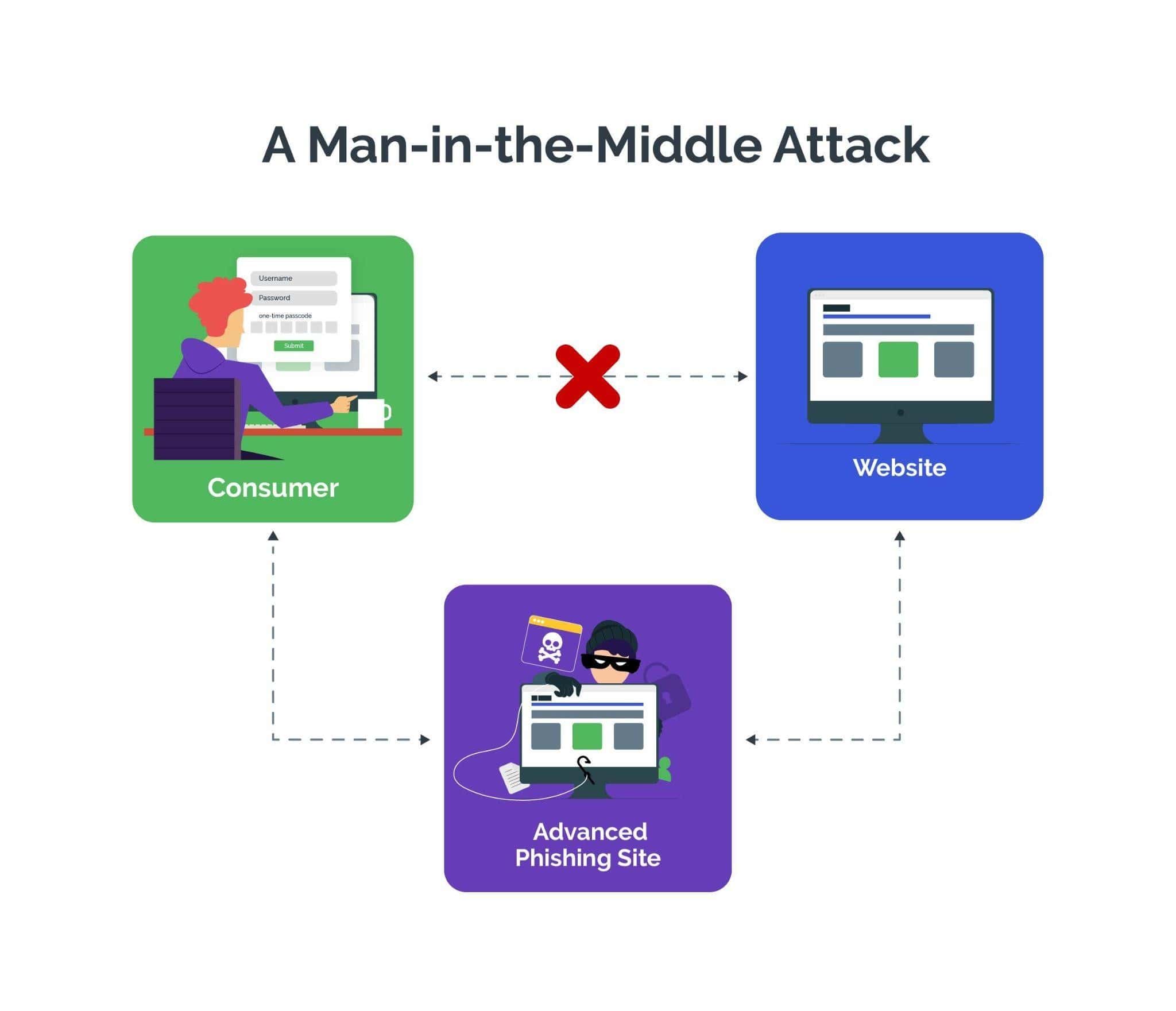
In one common scenario, attackers use advanced phishing sites (also known as reverse-proxy phishing sites) to lure victims into entering sensitive information, such as login credentials or multi-factor authentication (MFA) codes. These sites are designed to mimic legitimate websites almost perfectly, tricking users into believing they are interacting with the real site. As the user inputs their information, it is secretly transmitted to the attacker, who then can use it to access the victim’s accounts, initiate unauthorized transactions, or steal identities. Additionally, attackers might use this intercepted data to launch further attacks, deepening the breach's impact.
In other AITM attacks, bad actors use unsecured Wi-Fi networks, compromised routers, or malware installed on a victim's device to eavesdrop on sensitive information, like login credentials, financial details, or personal data, or to inject malicious content into the communication flow. They position themselves strategically between the sender and the intended recipient, to intercept and/or modify the data being exchanged. By manipulating the communication, attackers may deceive the parties involved into performing actions they wouldn't have otherwise, such as fraudulent transactions or money transfers.
Types of adversary-in-the-middle attacks
Adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) attacks may take various forms, with each type of attack targeting different specific communication protocols or vulnerabilities within a system. Some common types of AITM attacks include:
- Session hijacking: Attackers take over an ongoing session between the victim and a server using a stolen session cookie or session token to impersonate the victim and gain unauthorized access to their account or sensitive information.
- Packet sniffing: Hacker intercepts and monitors the network traffic passing between two parties to capture packets of data, enabling them to read private messages, extract sensitive information such as user credentials, financial data, or personal information.
- ARP spoofing: In Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) spoofing, cybercriminals intercept and modify the traffic between the sender and the intended recipient by manipulating the ARP cache of a victim's device or router to associate the attacker's MAC address with the IP address of another legitimate device on the network.
- DNS spoofing: In Domain Name System (DNS) spoofing, attackers can redirect users to fake websites or intercept their communications, by redirecting DNS queries to a malicious server controlled by the attacker.
- SSL stripping: Bad actor downgrades a secure HTTPS connection to an unencrypted HTTP connection to intercept and read the supposedly encrypted data exchanged between the victim and the server.
- WiFi eavesdropping: Attackers intercept WiFi communications and capture sensitive information transmitted over the network, such as passwords, emails, or financial transactions, by exploiting vulnerabilities in wireless networks or by setting up rogue access points.
How AITM phishing attacks work
Adversary-in-the-middle phishing attacks operate by positioning the attacker between the victim and the legitimate entity being impersonated, such as a banking website or an online service. This allows the attacker to intercept, capture, and manipulate the communication in real-time. Here’s a closer look at how these attacks typically unfold:
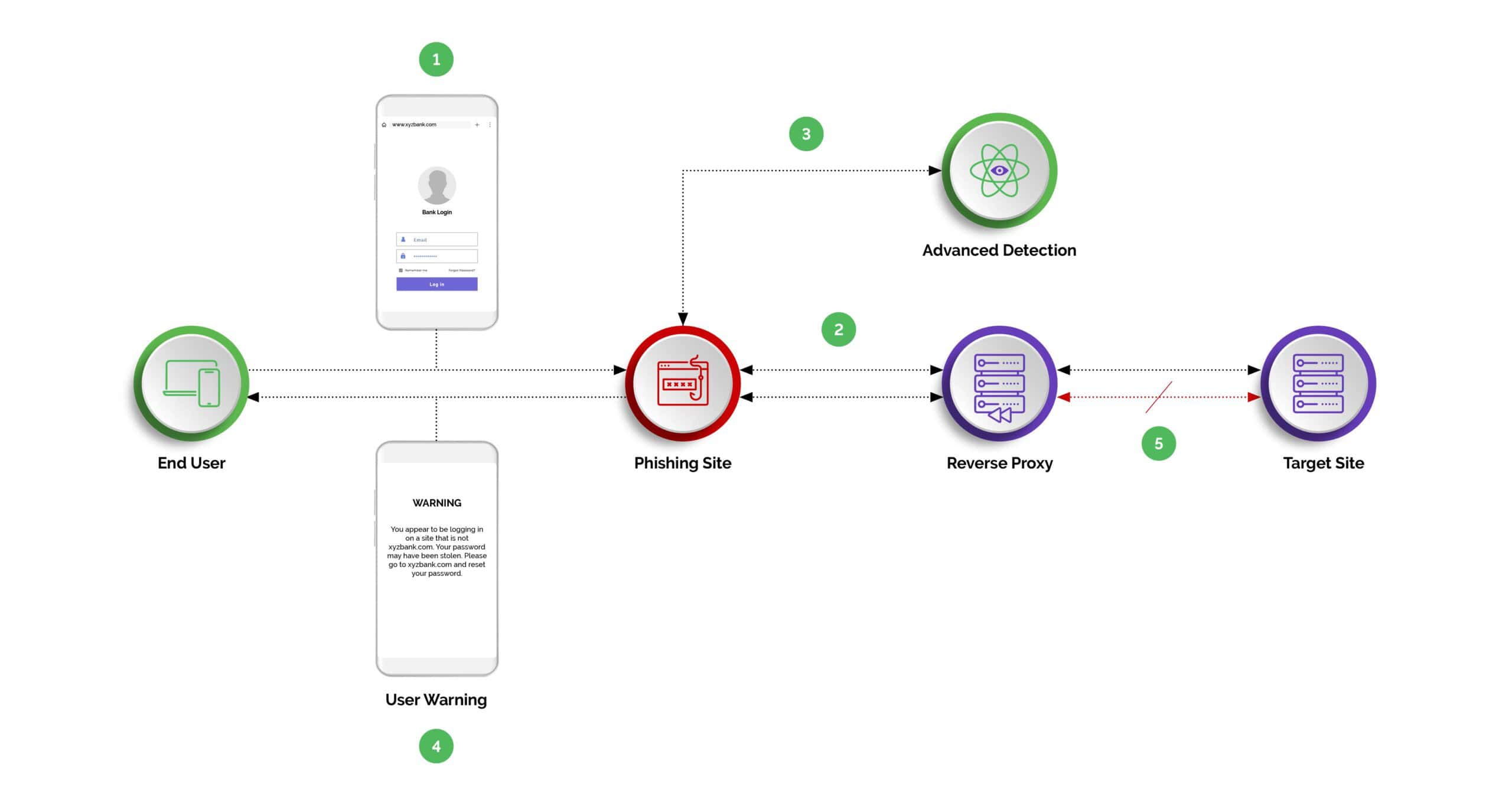
1. Setting Up a Phishing Site
The attacker sets up a malicious website that closely mimics a legitimate site that the victim trusts. This could be a bank, an email service, or any other online platform requiring login credentials.
2. Luring the Victim
The victim is lured to this phishing site through various means, such as a deceptive email, a text message, or even through compromised websites. These messages often create a sense of urgency, prompting the user to act immediately by clicking on a provided link.
3. Intercepting Communications
Once the victim attempts to log in or enter sensitive information on the phishing site, the attacker captures this data. However, unlike simple phishing schemes, in AITM attacks, the information is also relayed to the legitimate website in real-time. This means the attacker not only obtains the login credentials but also successfully logs in to the real site, bypassing two-factor authentication (2FA) or other security measures the user might have in place.
4. Session Hijacking
With the victim's credentials and active session information, the attacker can hijack the session. In some cases, they might manipulate the content of the communication, request additional information (like credit card numbers or social security numbers), or perform unauthorized transactions.
5. Covering Tracks
Throughout this process, the victim might remain unaware of the ongoing attack, as the attacker can relay content from the legitimate site back to the victim, creating the illusion of a secure connection. The attacker might also take steps to cover their tracks, making detection and response more challenging.
AITM attacks are particularly dangerous because they can circumvent traditional security measures like 2FA, SSL/TLS encryption, and others designed to secure the communication between a user and a website. To protect against AITM attacks, users are advised to verify the authenticity of URLs before entering sensitive information, use advanced security solutions like multi-factor authentication methods that are harder to intercept (such as app-based or hardware token 2FA), and stay educated about the latest phishing tactics.

Prime targets of adversary-in-the-middle attacks
Anyone engaging in online activities on the internet is at risk of being targeted by AITM phishing attacks. Adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) attacks are used to target a wide range of businesses across sectors. However, financial institutions and e-commerce platforms are particularly prime targets due to the potential value of the information they possess.
For instance, by targeting financial institutions, attackers seek to intercept banking transactions, steal financial credentials to gain unauthorized access to bank accounts, or conduct fraudulent activities. Similarly, by targeting e-commerce companies, bad actors try to compromise payment details, steal information on trade secrets, or manipulate transactions for monetary gain. Additionally, government departments, military organizations and critical infrastructure sectors are also prime targets due to the sensitive nature of the information they handle and the potential impact of disruption.
Risks associated with adversary-in-the-middle attacks
Adversary-in-the-middle attacks pose significant risks and can have far-reaching consequences for affected consumers and businesses. These attacks can result in data breach due to interception, theft of sensitive information exchanged between parties, and compromise of intellectual property. The intercepted data may include login credentials, usernames and passwords, personal information or financial data that may expose consumers and businesses to heightened risk of identity theft, financial losses, and other types of malicious activities.
Attackers often use AITM attacks for data manipulation, which can deceive or mislead users into performing unintended actions. Further, injecting malicious attachments, code, or content into web pages or email communications, can lead to malware infections, phishing attacks, or the distribution of fraudulent information. AITM attacks enable attackers to use this stolen information to manipulate transactions, redirect funds or alter critical data, leading to financial losses or reputation damage.
Not only do AITM phishing attacks undermine the trust in communication channels, breaches of confidentiality can result in legal liabilities, regulatory penalties, and reputation damage.
Telltales of adversary-in-the-middle attacks
Understanding the subtle signs of potential interception or manipulation of communication channels can help organizations identify AITM attacks. The key to identifying such attacks lies in vigilant monitoring of network behavior and traffic. Anomalies such as unexplained spikes in network traffic, unusual session durations, SSL certificate warnings or communications with known malicious entities can serve as significant indicators of an AITM attack in progress. Furthermore, discrepancies in user account activities, such as uninitiated account lockouts or unusual multi-factor authentication (MFA) alerts, also warrant closer investigation.
Methods to prevent adversary-in-the-middle attacks
To safeguard against adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) attacks, organizations must deploy a comprehensive strategy that strengthens every layer of their communication and network defenses.
Sophisticated phishing protection tools like Arkose Phishing Protection are engineered to combat advanced phishing strategies in real time — before the attacker has been able to take over an account — offering a solid line of defense against man-in-the-middle attacks and complex phishing efforts. These tools proactively monitor for such cyber threats, enabling quick actions to counter and mitigate their effects. By pinpointing and blocking attempts to steal login credentials, these software tools play a critical role in protecting users' sensitive information and blocking unauthorized entry.
Moreover, this type of software is adept at inhibiting the interception of codes used in multi-factor authentication (MFA) or two-factor authentication (2FA), enhancing the security measures around verifying user identities. It's also crucial in stopping the misuse of hijacked authentication tokens, thus strengthening the security framework of the system. Through the provision of tailored notifications, the software ensures that users stay alert to emerging threats, empowering them to take the necessary precautions to defend their personal and professional information.
Other key practices include employing robust encryption standards like TLS and SSL to secure data in transit, and utilizing digital certificates from reliable certificate authorities (CAs) to authenticate websites and secure connections. Networks should be securely configured and updated, with devices set up to minimize vulnerabilities and segmented to contain potential breaches. Strong authentication methods, including multifactor and biometric authentication, are essential to verify user identities and protect against unauthorized access. Regular security audits, prompt updates, and vulnerability assessments are crucial for identifying and addressing security gaps.
Additionally, educating users on the dangers of AITM attacks and instilling good cybersecurity habits can significantly reduce the risk posed by these threats, emphasizing the importance of vigilance in recognizing phishing attempts and maintaining secure connections.