What is a man-in-the-middle attack?
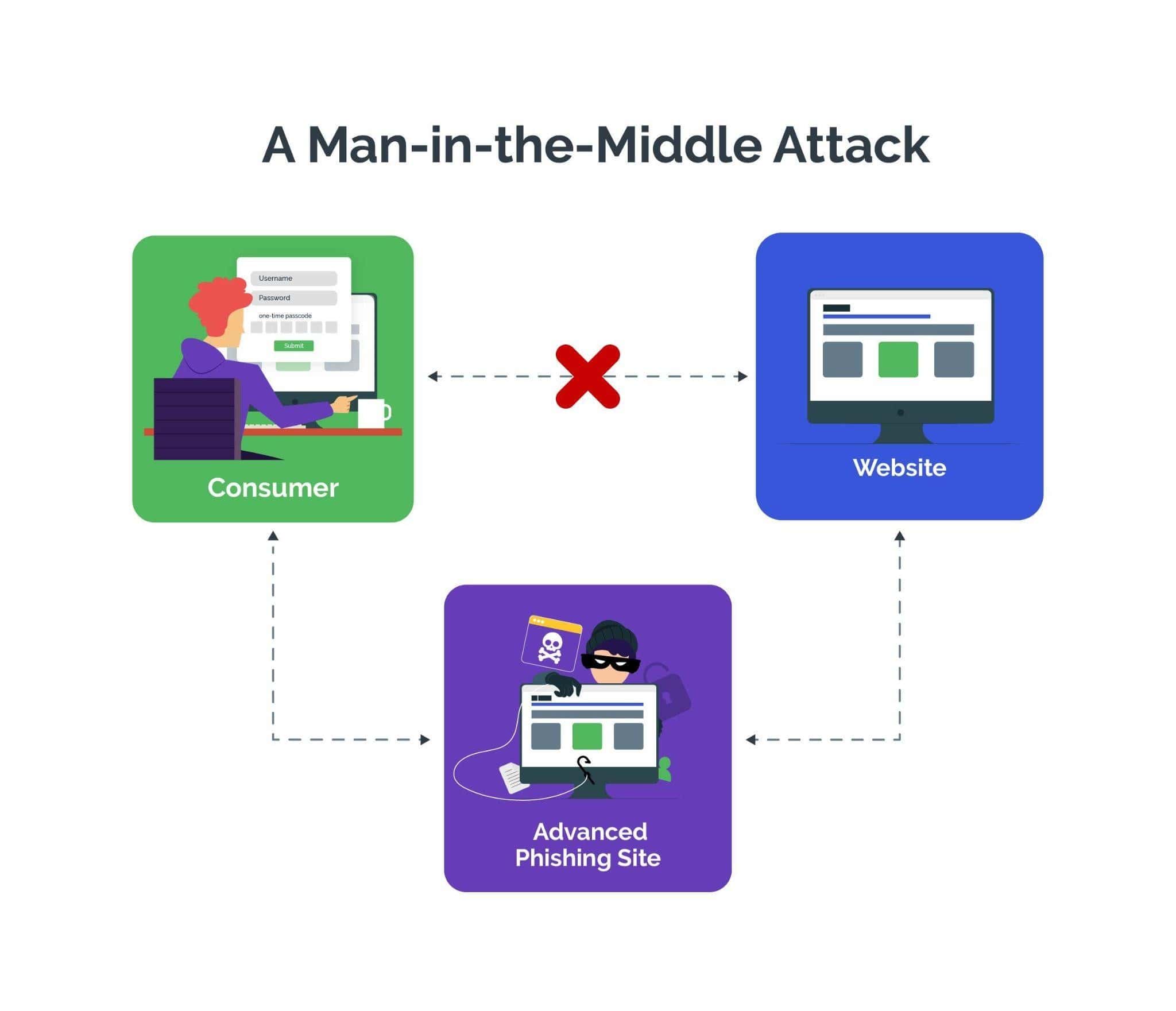
A man-in-the-middle attack is when a bad actor insidiously intercepts communication between a user and a legitimate website to steal the data exchanged between them. These attacks are also known as MITM or reverse proxy attacks and can result in theft of sensitive information like user credentials and MFA codes.
The Role of Reverse Proxy Sites in MITM Attacks
Reverse proxy sites facilitate man-in-the-middle attacks, also known as advanced phishing attacks, by acting as intermediaries between users and legitimate websites. These proxy sites intercept incoming requests from users and forward them to the real sites, enabling hackers to eavesdrop on the communication without the users' knowledge.
Cybercriminals insert these fake websites between the user and the legitimate website to intercept sensitive information such as login credentials, account details, financial information, or personal data. Since users are unaware that their communication is being captured by a third party, it makes it easier for attackers to steal sensitive data, exposing users to heightened security risks such as bank account takeover (ATO).

How Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Work
The key feature of a man-in-the-middle attack is a malicious actor intercepting communication between an unsuspecting user and a legitimate website. Attackers impersonate trusted entities or exploit the vulnerabilities in network protocols to launch MITM attacks.
By positioning themselves between these two communicating entities, hackers can snoop on the communication, modify the data exchanged, or insert their own malicious content. This allows them to steal personal information and use it for malicious activities.
Involvement of Bad Actors
By intentionally intercepting and manipulating communication between two parties, bad actors play a central role in man-in-the-middle attacks. These individuals not only exploit vulnerabilities in network infrastructure to compromise trusted entities, but also use deceptive tactics to position themselves as intermediaries. Bad actors steal sensitive information, compromise data, and exploit unsuspecting users for financial gain or other nefarious activities.
Classifying Different Types of MITM Attacks
Man-in-the-middle attacks can be broadly classified into two categories, namely: passive and active man-in-the-middle attacks.
Passive MITM attacks involve eavesdropping on communication without altering the data. On the other hand, in active man-in-the-middle attacks, bad actors not only intercept the data transferred between parties but also modify, manipulate, or inject malicious content into the communication stream.
Spoofing Attacks
Spoofing attacks when used in man-in-the-middle (MITM) scenarios can deceive victims into believing they are communicating with a legitimate entity. Using techniques like IP spoofing, where forged source IP addresses impersonate trusted devices or networks, attackers can intercept and redirect sensitive traffic.
IP and DNS spoofing allows MITM attackers to mask their true identity and mimic legitimate entities, enabling them to execute MITM attacks with increased efficiency.
Session Hijacking and Packet Injection
Using session hijacking, where an ongoing session between two communicating parties is overtaken illegitimately, attackers take control of the communication to access sensitive information. Session hijacking is a commonly used technique in man-in-the-middle attacks to intercept and manipulate data exchanged during the session.
MITM attackers use packet injection to insert malicious data packets into the communication stream, enabling modification or disruption of the integrity of the transmitted data. Packet injection can facilitate several forms of man-in-the-middle attacks such as data manipulation or denial of service.
Risks Associated with MITM Attacks
Due to interception and manipulation of sensitive communication, man-in-the-middle attacks pose significant risks to individuals and organizations. Man-in-the-middle attacks cause theft of confidential information such as passwords, financial details, or personal data, often resulting in identity theft, financial loss, or reputational damage.
Because MITM attacks facilitate the spread of malware or other malicious payloads and result in compromise of data integrity, they undermine the trust in communication channels and amplify the potential impact on impacted users and businesses.
Implications for Enterprises
Businesses face serious implications of man-in-the-middle attacks, including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Since MITM attacks result in compromise of sensitive business information, customer data, and intellectual property, businesses may face legal and regulatory consequences.
Man-in-the-middle attacks undermine the trustworthiness of enterprise communication channels, resulting in erosion of customer confidence and jeopardizing relationships with clients, partners, and stakeholders. Lack of trust in online platforms and services can impact customer confidence and potentially deter future interactions with affected businesses.
Risks for End Customers
End customers risk exposure of sensitive personal and financial information, such as passwords, credit card details, and private communications. This stolen information can compromise the security and privacy of users and expose them to heightened risk of identity theft, financial fraud, and unauthorized access to online accounts.
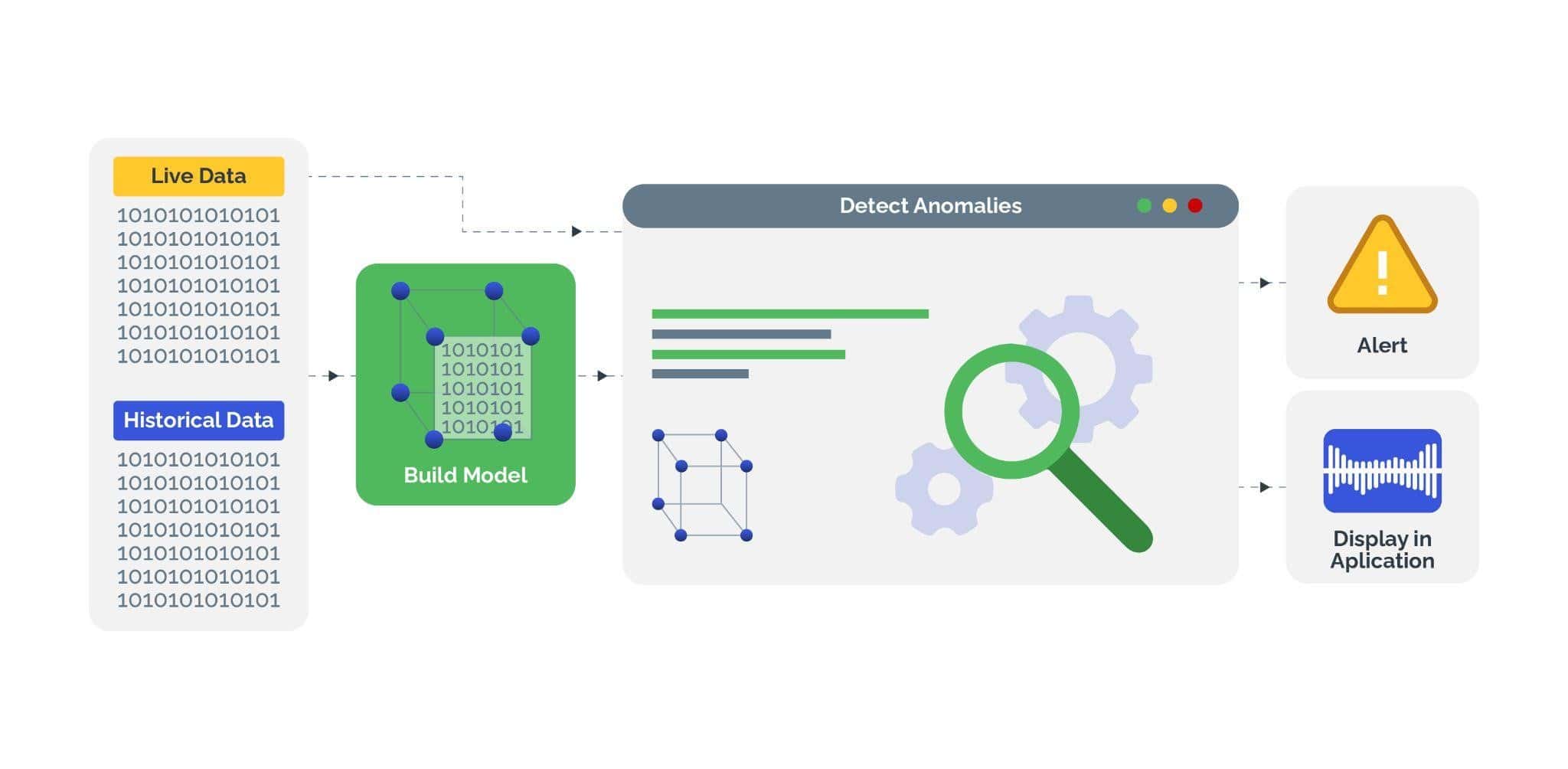
Steps to Detect MITM Attacks
To protect their networks and consumers from the aftermath of MITM attacks, businesses must detect and stop these attacks early in their tracks.
Some steps that organizations can take to detect man-in-the-middle attacks are:
- Implementing network monitoring tools to analyze traffic patterns and detect anomalies such as unexpected redirections or unauthorized devices accessing the network.
- Employing secure communication protocols like HTTPS connection.
- Using digital certificates to verify the authenticity of particular websites and detect attempts at interception or tampering.
- Regularly monitoring for changes in network configurations, such as unexpected changes in DNS settings or SSL/TLS certificate expirations.
Signs to Look Out For
For effective detection of man-in-the-middle attacks, businesses must look out for indicators of potential interception or tampering of communication, including:
- Unexpected browser warnings about invalid SSL certificates
- Unexplained changes in website behavior
- Suspicious network activity such as unexpected redirections or unusually slow connections.
- Discrepancies between the expected and actual content of websites, such as altered login pages or injected advertisements.
- Unrecognized devices or IP addresses accessing their network
- Inconsistencies in the information displayed in digital certificates
Role of Network Monitoring Tools
Network monitoring tools can play a crucial role in detecting man-in-the-middle attacks. By continuously analyzing network traffic for irregular patterns and anomalies, these tools can identify unauthorized devices attempting to intercept or manipulate communication, and trigger real-time alerts, enabling security teams to review the flagged activities.
Using network monitoring tools, organizations can quickly respond to MITM attacks, mitigate the risk of potential data breaches, and minimize the impact on network security and integrity.
Preventive Measures Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
By implementing effective preventive measures, businesses can protect their digital assets and ensure user security from man-in-the-middle attacks. Robust encryption protocols such as HTTPS connection can be effective in securing communication channels and preventing data interception.
Businesses can employ digital certificates and certificate authorities to verify the authenticity of websites, thereby reducing the risk of falling victim to spoofed or malicious domain names. User education programs about the importance of cybersecurity best practices, safe browsing habits, such as avoiding public Wi-Fi internet connections, and verifying website URLs, can help mitigate the risk of becoming a target of MITM attacks.
Utilizing Advanced Phishing Detection Software
Reverse proxy phishing protection software like Arkose Phishing Protection serves as a robust defense mechanism against sophisticated phishing tactics, particularly mitigating man-in-the-middle and advanced phishing assaults. This software operates by actively detecting such attacks in real-time, allowing for swift response and mitigation measures. By effectively identifying and thwarting attempts at credential theft, it serves to safeguard sensitive user information and prevent unauthorized access.
Furthermore, the software is equipped to halt the interception of multi-factor authentication (MFA) or two-factor authentication (2FA) codes, bolstering the security of authentication processes. It also plays a crucial role in preventing the exploitation of stolen authentication tokens, thereby fortifying overall system integrity. Additionally, users are kept informed and vigilant through customized alerts, ensuring they remain aware of potential threats and can take appropriate action to protect themselves and their data.
Importance of Strong Encryption and Secure Networks
Strong encryption and secure networks are paramount in mitigating man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. By ensuring that intercepted communication remains unreadable and tamper-proof to unauthorized entities, encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, safeguard data confidentiality and prevent MITM attackers from deciphering sensitive information exchanged between parties.
Secure networks with proper access controls and intrusion detection systems are better positioned to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate the risk of attackers infiltrating communication channels for MITM attacks.