What is card testing and how does it work?
Card testing is a form of card-not-present fraud where fraudsters try to determine the validity of stolen or generated credit card information by making small online purchases or transactions. Once valid credit card numbers are identified, fraudsters can use them for larger unauthorized transactions or other fraudulent activities.
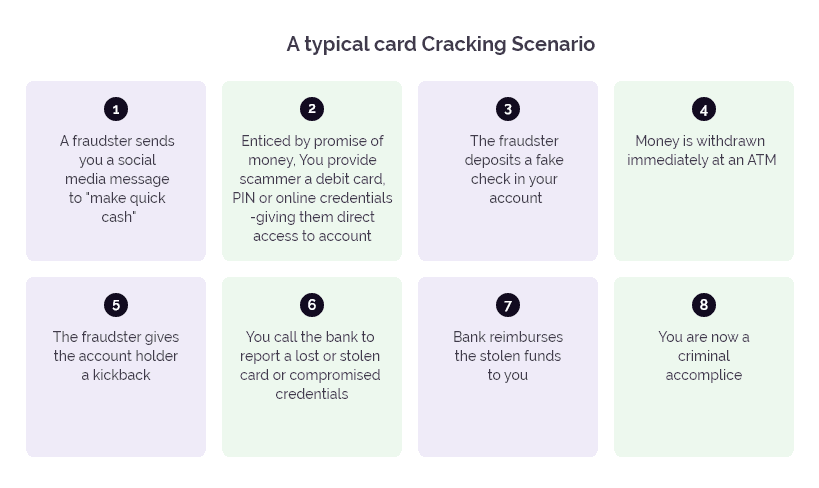
Card testing is also known as carding or card cracking. It can cause financial losses to businesses and consumers, if left unchecked.
Why is card testing a concern for businesses?
The exponential growth in the e-commerce market provides fraudsters with a wider horizon to execute card testing. Using bots and automation they can achieve scale, which can be a big headache for global businesses.
Card testing can have several negative impacts on businesses, especially on those that rely on online transactions. The biggest loss comes in the form of financial damage, as card testing is often used for unauthorized transactions. This means merchants are liable for chargebacks and refund the cardholder, in addition to incurring other types of fees. High rates of fraudulent transactions can result in businesses losing their payment processing services. Payment processors may terminate their relationship with a business if they perceive it as a high-risk merchant due to excessive fraud attacks.
Furthermore, credit card testing usually causes a large number of declines to be associated with your business, which damages the reputation of your business with card issuers and card networks. This can make all of your transactions appear riskier and result in an increased decline rate for legitimate payments, even after card testing fraud stops.
To deal with the aftermath of the attack, affected businesses must also allocate resources such as investing in fraud prevention tools and technologies, employing staff to monitor transactions for suspicious activity, and handling chargeback disputes.
Businesses may experience an influx of customer inquiries and complaints related to unauthorized transactions. Handling these inquiries can strain customer support resources and negatively impact the customer experience. These operational disruptions increase costs, erode profit margins, and disrupt cash flow.
Affected businesses that experience a high rate of fraudulent transactions can suffer damage to their reputation. Customers may lose trust in the business's ability to secure their payment data, resulting in a loss of customer confidence and loyalty. They may also face legal consequences as regulatory authorities may investigate security breaches and subject the business to fines or legal action.
The mechanisms behind card testing
Cybercriminals employ a series of steps to determine the validity of credit card information. These steps are as described below:
- Cybercriminals acquire credit card data through various means. This may include purchasing it from the dark web, stealing information through phishing attacks, or using card generation algorithms to create random card numbers.
- To verify the validity of card data and determine if they can be used for fraudulent purposes, attackers test the cards using bots, automated scripts, and also manual methods. They may check the Issuer Identification Number or IIN, also known as the Bank Identification Number or BIN, validity of card's expiration date, and the Card Verification Value (CVV) or Card Verification Code (CVC) associated with the card.
- Once fraudsters have identified the potentially valid cards, they make small transactions on e-commerce websites or payment platforms to test if the card is active and functional. These transactions are usually for low amounts to avoid raising suspicion. Fraudsters can then use these valid card details for more significant unauthorized purchases, cash withdrawals, or other forms of fraud until the cardholder or financial institution detects the bogus activity. They, however, use techniques like proxy servers, VPNs, or other methods to obscure their IP addresses and locations to avoid detection.
In recent years, the easy accessibility to commoditized bots is enabling attackers to quickly execute bot-driven attacks at scale. Bots and a network of bots, botnets, can play a significant role in card testing, as they provide attackers with a vast and distributed network of compromised devices, which can be harnessed to automate and scale card testing activities. This means, using botnets, attackers can simultaneously test numerous credit card numbers across various online platforms and merchants, increasing the chances of finding valid card information. Further, by distributing the computational workload across the networked devices, bots allow cybercriminals to perform card cracking more efficiently and quickly.
Botnets can add a layer of anonymity to card testing operations as the traffic originates from a variety of different IP addresses, which makes it difficult for security systems to trace them back to a specific source. Cybercriminals also use botnets to evade security measures, such as rate limiting and IP blocking, implemented by online merchants and payment processors to detect and prevent card cracking attempts. By spreading the testing across multiple devices and IP addresses, botnets make it harder for automated security systems to flag suspicious behavior.
Attackers often use botnets to launch phishing attacks to collect credit card information and other sensitive data directly from unsuspecting individuals. They depend on automated bot attacks for Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) to distract and overload security teams, making it easier for cybercriminals to carry out card testing, credential abuse, and other fraudulent activities undetected. These attacks not only result in a huge revenue hit from authorization processing fees but also cause serious brand damage to businesses. This can have long-lasting negative effects on the reputation and trustworthiness of the company, leading to potential customer loss and financial repercussions.
The red flags of card testing attacks
Detecting card testing attacks can be challenging. However, there are several telltales that can help businesses identify potential carding activity. Combining these indicators with comprehensive credit card fraud detection software and data analysis, businesses can monitor patterns, continuously update fraud detection measures, and mitigate card testing attacks effectively.
Some of the common indicators of card testing attacks include: unusual transaction patterns, common purchase amounts, use of sequential or predictable card numbers, IP address anomalies, geographic inconsistencies, multiple failed authorization attempts, and a sudden rise in new customer accounts with similar or suspicious email addresses, among others.
Active monitoring and analysis of payment data for anomalies and specific behaviors can be useful in recognizing suspicious transaction patterns, indicative of card testing attempts. Businesses must consider setting baseline metrics for legitimate transaction behavior, including average transaction amount, transaction frequency, and typical geographic locations of customers. Any deviation from these specified standards can be construed as indicators of suspicious activity.
They should monitor small, low-value transactions, especially those with round numbers (e.g., $1, $5, $10), as a sudden spike in such small purchases could be an attack attempt on an unsuspecting merchant’s site. Another indication of card testing attempts is the use of sequential card numbers or card numbers with easily guessable patterns (e.g., 1234 5678 9101 1121). Card testers often use such patterns when generating or testing card numbers.
Rapid transaction sequences, where multiple transactions occur within a short time frame, often in quick succession, could be a potential card testing attempt. Card testers aim to process as many transactions as possible in a short period. Frequent authorization attempts with different card numbers and frequent use of incorrect CVV/CVC codes can be indicative of testing for valid cards.
Businesses must inspect transactions with billing and shipping addresses that do not match or appear inconsistent. Multiple transactions with different shipping addresses for the same card can be a red flag. Similarly, transactions from countries or regions that the business does not have a presence in could indicate use of proxies or VPNs to obscure their geographic location.
A surge in account fake account registrations with similar email addresses or phone numbers or frequent changes to account information should be looked at with suspicion. So should high volumes of transactions from a single source within a short time.
Mitigating the risks of card testing
Card testing can be particularly damaging for businesses that process online payments. Therefore, it is critical that these businesses adopt effective fraud mitigation measures to minimize the risks of card testing attacks and protect their business, customers, and financial reputation.
Implementing effective fraud prevention measures is crucial to protecting businesses from financial losses and reputational damage. Some of the ways businesses can mitigate the risks of card testing are as described below:
- Strong Authentication: Use strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) for customer verification. These measures add an extra layer of authentication, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting on transactions to prevent multiple attempts from a single source in a short time
- Transaction Monitoring: Continuously monitor transactions for suspicious patterns and high-risk activities.
- Address Verification (AVS) and CVV Verification: Require customers to provide the Card Verification Value (CVV) or Card Verification Code (CVC) during transactions. Use Address Verification Service (AVS) to verify that the billing address matches the cardholder's address on file.
- Geolocation Verification: Verify whether the transaction location matches the cardholder's typical geographic location and review transactions from unusual or high-risk locations.
- Account Behavior Analysis: Monitor consumer account behavior for changes or anomalies, such as frequent updates to account information or a sudden increase in transaction activity.
- Data Encryption: Consider using encryption protocols such as SSL encryption to ensure that sensitive payment data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Transaction Risk Scoring: Use a risk scoring system that assigns scores to transactions based on various factors (e.g., transaction amount, IP address, geographic location), which helps automatically flag or review transactions with high-risk scores.
- Machine Learning and AI-Based Fraud Detection: Deploy machine learning and artificial intelligence-based fraud detection software that can analyze large datasets and detect complex patterns of fraudulent behavior.
- Bot Management: Consider using third-party fraud prevention tools and services that specialize in detecting and preventing online fraud. Look beyond legacy CAPTCHAs. Implement effective bot management solutions that can identify and block malicious bot traffic.
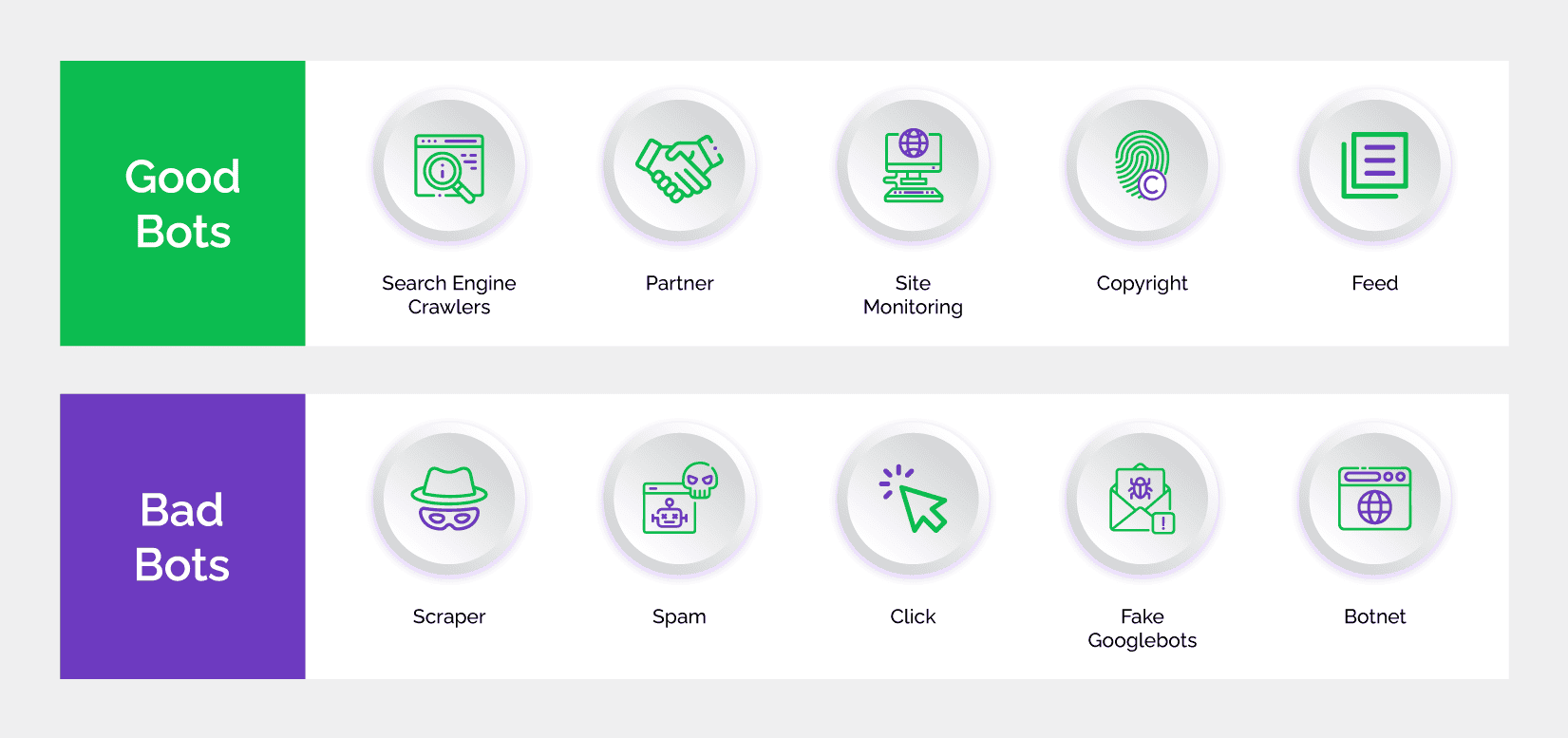
- IP Address Blocking: Block or restrict IP addresses associated with suspicious or known malicious activity.
- Collaboration with Payment Processors: Implement fraud prevention measures and share information on emerging threats with payment processors and financial institutions.
- Compliance with Security Standards: Adhere to industry security standards and regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Regularly assess and validate compliance.
- Review and Analysis of Data: Continuously review and analyze transaction data for patterns and trends related to card testing and other fraud activities to keep the fraud prevention measures up-to-date.
Effective strategies to prevent card testing
Preventing these types of attacks requires a multi-layered approach that combines technical measures and proactive monitoring. A multilayered security approach can enable businesses to create a more resilient defense against evolving card testing tactics. By implementing effective strategies and adopting a proactive approach to fraud prevention, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of card testing attacks.
Some strategies businesses should consider:
- machine learning-powered fraud prevention solutions
- web application firewalls (WAFs) and intrusion detection systems
- robust access control and web authentication
- encrypted data
- well-managed mobile devices
- Well-considered third-party risks
- up-to-date systems
- regular audits and reviews
- collaboration with peers /share threat intelligence
In addition to deploying fraud prevention solutions, businesses must regularly monitor all user activity for early detection of any card testing attempts, appropriate response, and adaptation.
Continuous monitoring allows businesses to proactively identify and mitigate card testing attempts before they can escalate into significant security incidents. With regular monitoring of transactions and network traffic, businesses can detect unusual or suspicious patterns promptly. This includes rapid and frequent small transactions, multiple failed authorization attempts, transactions from unfamiliar or high-risk locations, and the use of charge-back analytics. It also helps detect anomalies and deviations from established baseline behavior that triggers alerts for quick further investigation. Consistent review of transaction data, including the analysis of chargeback patterns, can provide a better understanding of normal transaction patterns and quickly identify deviations that may indicate card testing attempts.
With regular monitoring, businesses can respond rapidly to any suspicious activity and minimize potential damage. It also enables businesses to keep track of evolving attack techniques and adapt their strategies for future-ready protection. Regular monitoring data can be integrated with fraud detection systems and machine learning algorithms, enhancing their ability to identify card testing attempts and other fraudulent activities.
Many regulatory standards and compliance frameworks require regular monitoring of network and transaction data to detect and prevent fraud. Meeting these requirements helps ensure data security and regulatory compliance.
What's next after detecting a card testing attempt?
After detecting a card testing attempt, it's important to immediately mitigate the risk to prevent further damage and potentially identify the attackers. Isolate the affected system or network segment by suspending or blocking the source of the attack to prevent the attacker from further accessing or compromising other systems and data.
Proactive bot protection measures can help fight bot-driven card testing attacks, before they can achieve scale and increase the damages. Although many businesses use CAPTCHAs to fight bots, these legacy CAPTCHAs fall short in providing the level of security modern businesses need. Since CAPTCHAs have failed to keep pace with the advancements in bot technology, they cannot effectively stop intelligent bots from creating havoc. As a result, instead of effectively protecting from bots, outdated CAPTCHAs make the business vulnerable to card testing attacks and add to the overall costs. To enhance security measures, businesses should consider implementing some type of CAPTCHA into their checkout flow. This technology has improved in recent years and can produce much less friction to customers than previous versions.
Therefore, businesses need smart bot management solutions that can identify and stop the most advanced human-like bots early in their tracks, without degrading user experience for legitimate consumers.
How Arkose Labs Can Help Fight Card Testing Attempts
Arkose Labs specializes in bot management to provide businesses with future-proof protection from automated bot attacks including card testing. Arkose Bot Manager is an innovative solution that empowers global businesses to comprehensively beat the bots and provide long-term protection from automated card testing attacks.
Instead of blocking any incoming user, Arkose Labs offers them an opportunity to prove their authenticity. On the basis of real-time risk assessment, users are administered Arkose MatchKey challenges. This targeted friction ensures risky users face hurdles, while genuine users can continue with their digital journeys unhindered.
While bots of all levels and automated scripts fail instantly, malicious human attackers are engaged in a long-drawn battle requiring them to clear a deluge of challenges that keep increasing in complexity. The rising investments in the form of time, effort, and resources render the attack financially non-viable, which forces the attackers to give up for good.
Arkose Labs backs its partners with a 24x7 SOC support, data-backed insights and global threat intelligence to help them stay informed about emerging card testing tactics and adapt accordingly for long-term protection.