What is SMS security and why is it important?
SMS security is a term used to describe the measures put in place to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the Short Message Service (SMS) communications channel. It is important because SMS is commonly used for sensitive information such as two-factor authentication (2FA) codes, making it a target for hackers.
SMS: A multi-purpose tool with inherent risks
SMS serves as a fast and cost-effective messaging tool for purposes like two-factor authentication, emergency alerts, and remote work communication. However, it's not without risks. For example, SMS is a common target for phishing and smishing attacks. In SMS toll fraud, attackers use bots and scripts to abuse business SMS workflows and trigger fraudulent SMS messages to international or premium rate numbers. Bad actors sometimes collude with mobile network operators (MNOs) and share the illicit revenue while businesses are stuck with the bill.
Therefore, ensuring the reliability and security of SMS communications is crucial. SMS security measures, which include smart bot management solutions along with end-to-end encryption, secure transmission protocols, multi-factor authentication, web application firewalls (WAFs), and employee training, are critical to protecting consumer and business interests.
How SMS authentication works
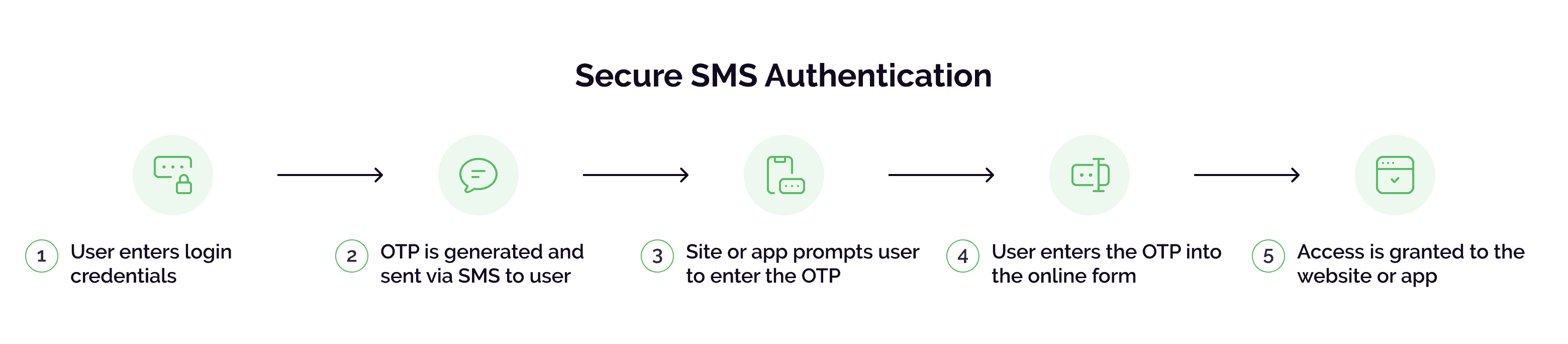
SMS authentication is a form of 2FA, which adds an extra layer of security to the user authentication process. A one-time code is sent to the user's mobile phone via SMS, which they must enter to confirm their identity. Even if an attacker obtains a user’s password, the bad actor would still need to provide the code or one-time password (OTP) to complete the login process or transaction, a difficult hurdle to overcome.
The steps involved in SMS authentication are as follows:
- Login: A user provides the username and password to initiate the login process on a website or mobile app.
- OTP Initiation: A unique, time-limited OTP is generated and sent to the user's registered mobile phone number via SMS.
- Verification: The site or app prompts the user to enter the verification code or OTP.
- Entering OTP: The user enters the OTP from the SMS into the provided field on the login page.
- Validation: The service validates the user-entered OTP and grants access if it matches with the one sent by the service.
Benefits of SMS authentication for enhanced security
There are several benefits of using SMS authentication to enhance SMS security. Some of the advantages include:
- Extra L ayer of Security: By adding an additional layer of protection to password, SMS authentication makes it difficult for attackers to exploit the login process for account takeover attacks. SMS authentication can also be used as part of a larger MFA strategy, where multiple authentication factors are used in combination.
- Easy, Cost-Effective Implementation: SMS authentication is generally cost-effective and easy to implement, as SMS is readily available from mobile carriers and does not require any special software or hardware.
- Accessibility: A large section of consumers use mobile phones, which makes SMS messaging widely accessible.
- Familiarity: Most consumers are familiar with receiving and sending text messages, which makes SMS authentication a method they are comfortable with and likely to understand.
- Quick Verification: SMS authentication is a fast process, as codes and OTPs are usually delivered within seconds.
- Regulatory Compliance: By facilitating user authentication and data protection in highly-regulated industries, SMS authentication can help comply with regulatory requirements.
- Security Awareness: Organizations can use SMS authentication to raise awareness about the importance of strong authentication and security practices among their users.
Common Methods of Implementing SMS Authentication
Businesses must consider several factors when implementing SMS authentication. These include reliability of SMS delivery, user experience, security, and compliance with data protection regulations. Businesses may need to integrate a combination of technologies and processes for secure delivery of codes and OTPs. For higher-security needs, businesses should consider supplementing SMS authentication with advanced authentication methods, such as app-based authenticators or hardware tokens.
Some common methods used to implement SMS authentication are:
- In-House SMS Gateway: Some organizations build in-house SMS authentication systems, where they develop and manage the SMS gateway themselves.
- SMS Service Providers: APIs from third-party SMS service providers can be integrated into business authentication systems.
- Authentication Services: Cloud-based Authentication as a Service (AaaS) allows organizations to integrate authentication services into their applications with little to no development effort.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Systems: IAM platforms can be integrated into applications and services to add SMS-based 2FA.
- Security Tokens: Some businesses issue hardware tokens to users that generate OTPs. These tokens can be synchronized with the authentication server and used as a second factor.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Solutions: Specialized MFA solutions often support a variety of authentication factors.
- Mobile App Integrations: Some organizations create custom mobile apps for their users that generate OTPs for authentication.
- Biometric Verification: SMS authentication may be combined with biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, to provide a higher level of security.
- User Verification Services: These services specialize in user registration and verification, enabling businesses to send SMS messages for user authentication.
- SIM Card Security: Implementing additional security measures with mobile carriers can help prevent SIM card swapping attacks.
Best Practices for Secure SMS Verification
SMS verification is widely used to enhance user account security. However, it has some limitations and vulnerabilities. Organizations would do well to stay vigilant and upgrade their SMS verification systems to adapt to the emerging threats. They must consider using authentication methods depending on specific use cases, risk appetite, and data protection policies.
To minimize the risk of unauthorized access or security breaches, businesses must follow the best practices of implementing secure SMS verification. Some key considerations for secure SMS verification include:
- Strong Passwords: Use SMS verification to complement, not replace, strong password policies. Ensure that consumers use strong, unique passwords for their accounts.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Combine SMS verification with another authentication factor, such as a password or biometric verification, for an added layer of security.
- Limited SMS Validation Attempts: Set a maximum number of attempts for SMS validation to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Time Limits for Codes: Ensure that the codes or OTPs sent through SMS expire after a defined time period, typically a few minutes, to reduce risk if the code is intercepted.
- Rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting to specify the number of SMS verification requests a user can make within a given time frame.
- Continuous Monitoring: Monitor authentication attempts continuously to identify unusual patterns or a high number of failed attempts.
- Reliable Providers: Choose reliable and secure SMS gateway providers with a track record of security and reliability.
- Sensitive Data Encryption: Protect user information both in motion and at rest, using data encryption technologies such as SSL encryption.
- Additional Security Measures: Consider complementing measures to protect users from phishing attempts and SIM swap attacks.
- Regulation Compliance: Be aware of and comply with data protection regulations that govern SMS-based authentication.
- Reviews and Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address possible weaknesses in the SMS verification process.
- Patches and Updates: Keep all software, including the SMS authentication system, up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- User Education: Educate users about best practices for SMS security.
- Recovery Plans: Develop a recovery plan in case of SMS authentication failures, and provide users with a way to regain access to their accounts securely.
Additional Measures to Enhance SMS Security
To enhance SMS security, businesses need additional measures beyond the basic implementation of SMS authentication. However, they must strike a balance between security and user experience to ensure that additional security measures do not introduce unnecessary friction for genuine users.
To supplement SMS security, business can consider using additional measures:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Include SMS as one factor and require a second factor, such as a password, PIN, fingerprint, or app-based authenticator, to add an extra layer of security.
- App-Based Authenticators: Generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs), which are more secure than SMS codes.
- Hardware Tokens: Generate secure one-time passwords for a reliable second factor for high-security applications.
- User Behavior Analysis: Detect suspicious activities, such as multiple failed login attempts, and trigger additional security measures.
- Geolocation Verification: Cross-reference user location with the location of their mobile device to detect potential unauthorized access.
- Rate Limiting and Lockouts: Implement rate limiting and account lockouts after a certain number of failed authentication attempts to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Fraud Detection Services: Identify and block suspicious SMS traffic and fraudulent activities.
- Secure Delivery Channels: Use secure channels such as encrypted SMS gateways to protect the transmission of SMS codes.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies in conjunction with SMS authentication.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees and customers about the risks and best practices associated with SMS security.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities in SMS Security
Businesses can implement the best practices described above to mitigate security risks, but no authentication method is 100% foolproof. Some of the potential risks and vulnerabilities in SMS security are as follows:
- SMS Toll Fraud: SMS toll fraud involves attackers using bot traffic to exploit the SMS workflows of victim businesses by initiating thousands of SMS messages to premium-rate numbers, and the bad actors collude with rogue MNOs to share the illicit revenues generated. The use of bots allows attackers to scale up the attacks in no time, increasing their financial gain and causing losses to the targeted business in the form of inflated telecom bills.
- SMS Interception: Attackers eavesdrop on SMS messages and intercept them during transmission.
- SIM Card Swapping: A type of identity theft, SIM swapping involves attackers fraudulently requesting a new SIM card with the victim's phone number to take control of the phone number and receive SMS codes to impersonate the victim.
- Smishing: Attackers may send fraudulent SMS messages, purportedly from trusted businesses that recipients are familiar with, and trick them into revealing sensitive personal and financial information.
- Sender ID Spoofing: Attackers can spoof the sender information in SMS messages to make it appear as if it’s coming from a legitimate source.
- Social Engineering: Attackers may manipulate users to reveal SMS verification codes or other sensitive information.
- Malware Distribution: Attackers can lace SMS messages with malicious links to direct users to fake websites or malware-infected apps, leading to interception of SMS messages or the compromise of user device or data.
- Lack of Encryption: Typically SMS messages are not encrypted, which makes them vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access.
- Carrier Vulnerabilities: Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in carrier systems or network infrastructure to breach security of SMS messages.
SMS Toll Fraud: An Evolving SMS Fraud Tactic
Attackers are continuously evolving their attack tactics to execute targeted and novel attacks. In addition to traditional attacks such as phishing, smishing, SIM swap, spoofing, and others that have SMS at the core, they are now targeting the SMS workflows of businesses to trigger massive volumes of SMS messages that terminate on premium-rate numbers. Why? Because telecom charges for premium numbers are massively greater than those of non-premium numbers; this allows the attackers to multiply their financial gains as they collude with rogue MNOs to share in the illicitly gained profits.
These automated bot attacks initiate thousands of SMS messages by inputting premium-rate numbers in the mobile phone field when prompted. Once the SMS messages are initiated, it is well-nigh impossible for the business to retract them.
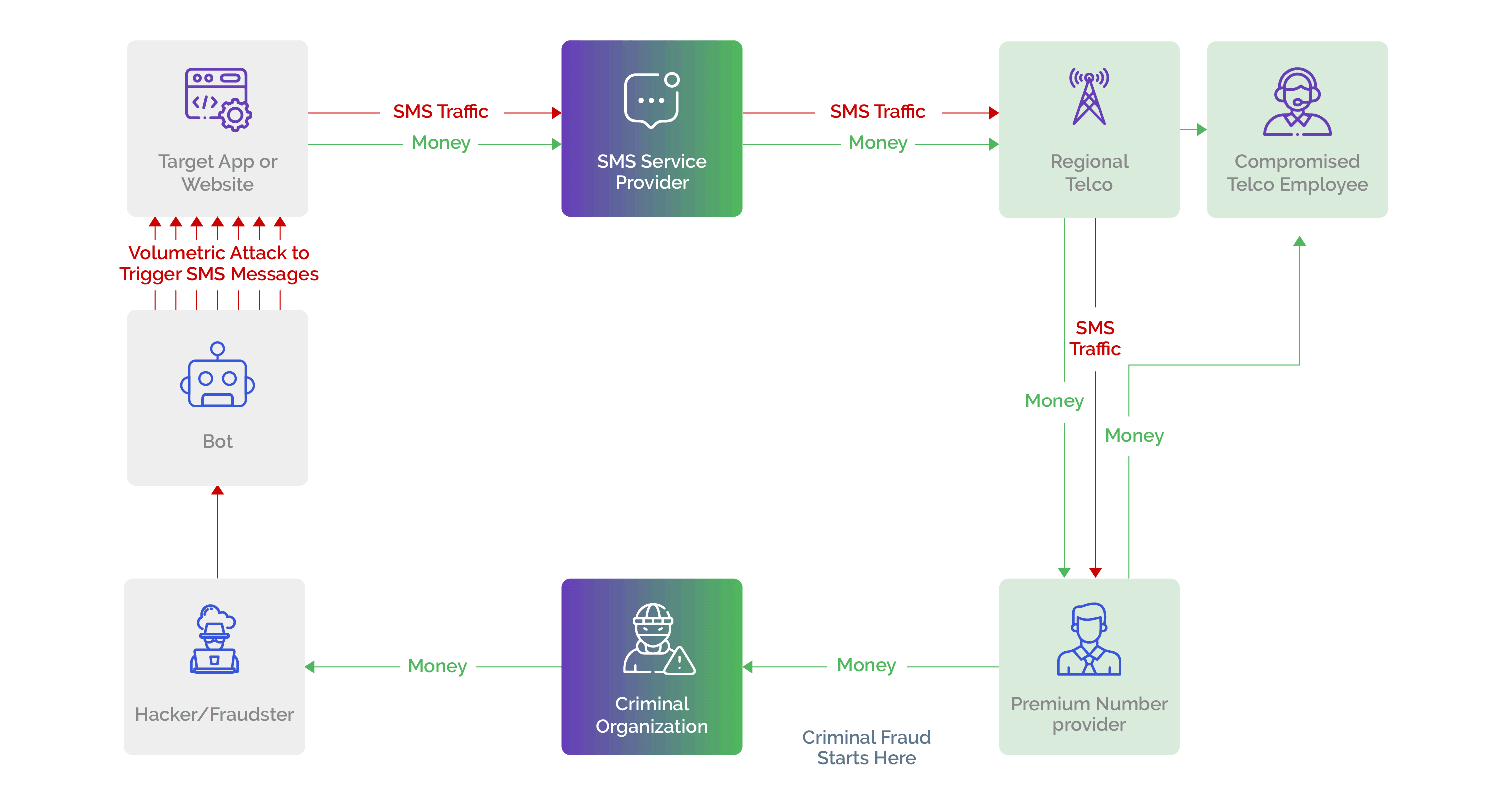
Even cloud-based security systems that most telecom operators use cannot stop these SMS messages. The business realizes that it has been attacked only when it receives a highly exaggerated telecom bill. As a result, the affected business has few options except to absorb the losses.
Fortunately, businesses can prevent SMS toll fraud by implementing smart bot management solutions, such as Arkose Bot Manager, which identify bots early in the process and prevent them from triggering the SMS flow. Since automated traffic bots cannot manipulate the SMS page to artificially inflate the traffic, it helps protect the SMS workflows from potential abuse and saves spurious telecom costs.
Case Studies of the Successful Implementation of SMS Security Measures
SMS-based security measures can be valuable components of a broader security strategy to protect users and their data. Coupled with other security measures, SMS-based authentication is enabling organizations across industries to improve SMS security.
A case in point is Snapchat, a leading social media platform with nearly 400 million users across the world. The company was facing a deluge of bot-driven attacks that were exploiting its user verification SMS workflows. Snapchat was looking for a new approach to bot management and account security, so it turned to Arkose Labs to help protect its consumers and reduce fake account creation on the web.
Within a short period of deployment, Arkose Labs was able to make a major impact, allowing Snapchat to detect more critical risk log-in attempts on the web, reduce attempts to create fake accounts, and drive down SMS toll fraud charges, while maximizing its return on investment.

Arkose Labs for Comprehensive Protection from SMS Toll Fraud
Arkose Labs is helping leading global businesses, including Fortune 500 companies, to successfully ward off automated SMS toll fraud attacks. Arkose Bot Manager is a smart bot protection solution that accurately identifies bots and automated scripts and stops them before they can reach or exploit the SMS workflow.
Arkose Labs allows every incoming user to prove their authenticity, thereby ensuring that no potentially revenue-generating customer is lost due to outright blocking. Depending on the real-time risk assessment, users face challenge response authentication in the form of Arkose MatchKey challenges. While bots and scripts fail instantly, good users can continue with their digital interactions unobstructed. However, malicious humans and click farms face a barrage of challenges that keep increasing in complexity, and increasing the effort, time, and resources to solve these challenges at scale. In view of depleting returns, attackers abandon the attack and move on.
Arkose Labs shares data-backed insights, global threat intelligence and provides 24x7 SOC support to its partners, enabling them to mitigate threats as soon as they are detected. Arkose Labs backs its solution with a $1M warranty against SMS toll fraud attacks, ensuring its partners long-time protection from automated SMS toll fraud attempts and inflated telecom bills.