What is banking new account fraud detection?
Banking new account fraud detection involves identifying and mitigating the creation of illegitimate accounts on financial platforms. Bad actors create accounts using stolen or synthetic identities to exploit them for money laundering, fraudulent transactions or other financial crimes. Robust cyberattack prevention mechanisms monitor systems and flag suspicious new account registration activities.
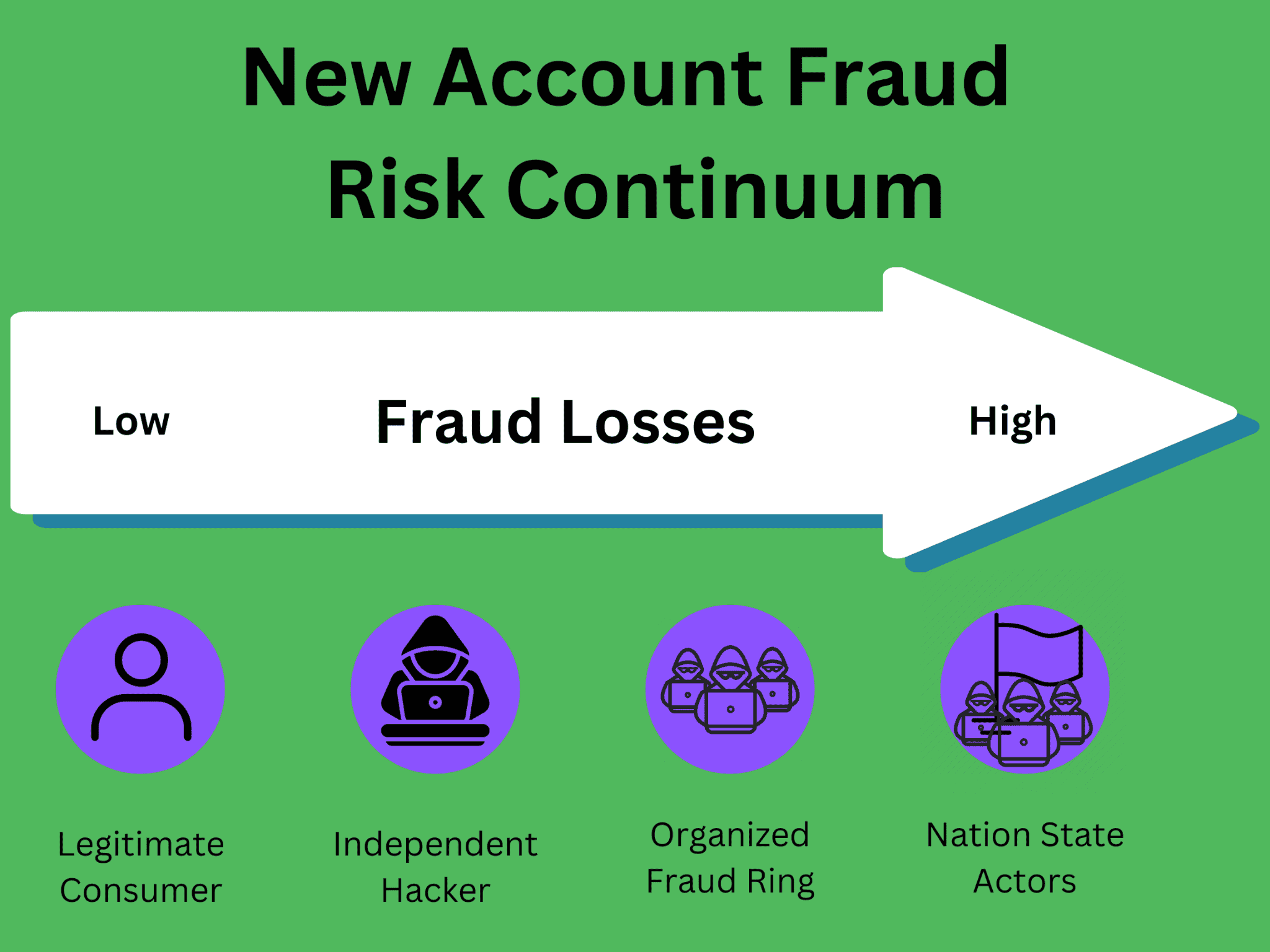
Fraudulent new accounts can cause colossal financial losses for both the bank and its consumers, making fake account detection crucial for maintaining user account security and business integrity.
How banking new account fraud takes place
New account fraud in banking often begins with fraudsters obtaining consumers’ personal information through data breaches, social engineering, advanced phishing or by purchasing stolen data on the dark web. Combining stolen and fake user information, fraudsters create synthetic IDs to open new accounts with financial institutions. These fraudulent accounts may include savings accounts, checking accounts, credit cards or loans.
Once fake accounts are registered, fraudsters can engage in various criminal activities, including making unauthorized transactions and exploiting the credit lines associated with these accounts. Because fraudsters use sophisticated tactics to fool security teams, detection is often challenging.
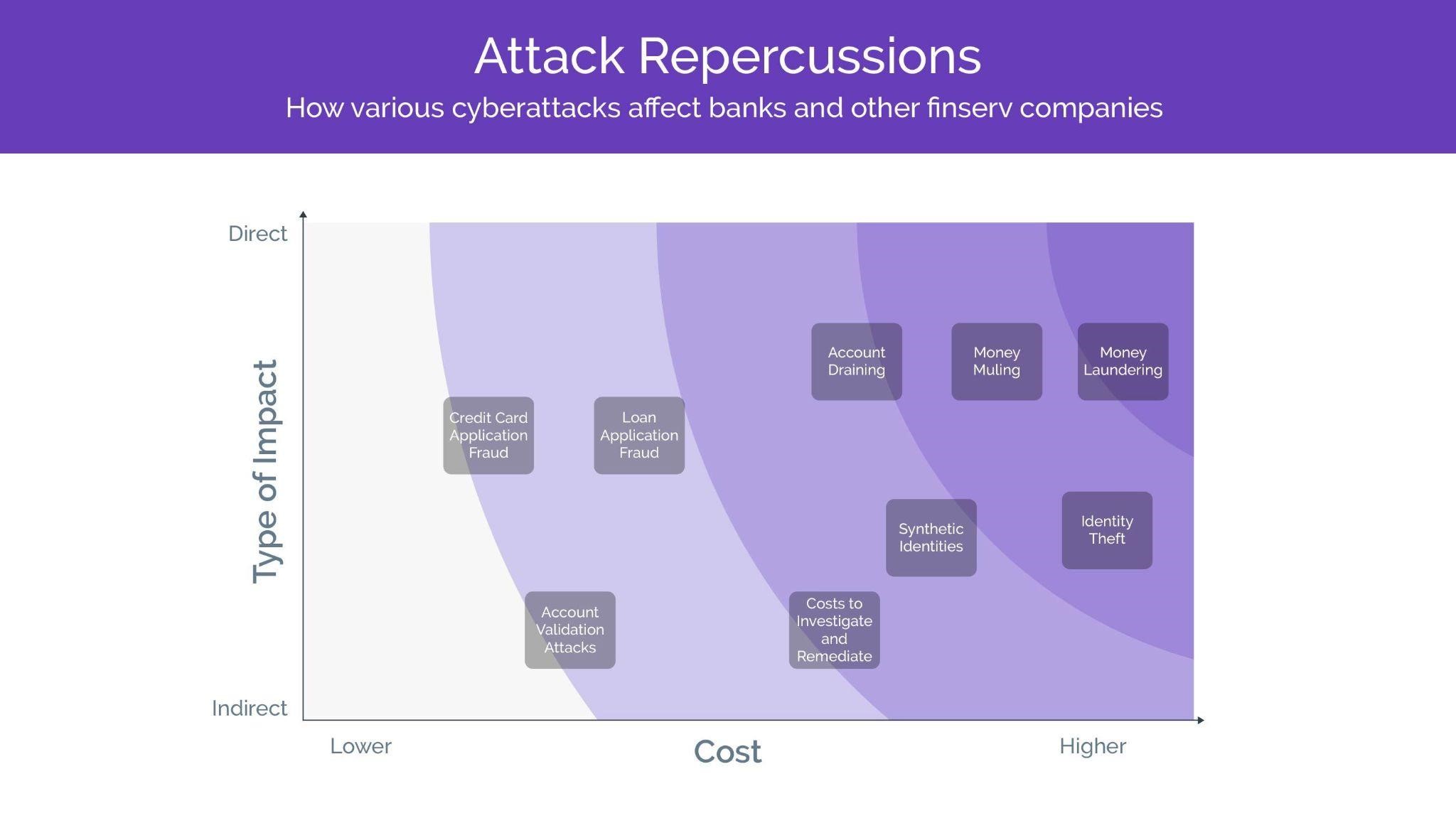
Examples of fake account fraud in banks
Cybercriminals generally exploit fraudulent new accounts opened in banks through the following ways:
- Deposit of counterfeit checks: Deposit counterfeit checks or fraudulent money orders and quickly withdraw the money before the bank realizes the checks are fake.
- Money laundering: Funnel illicit funds through these accounts by obscuring the source of the money and making it appear legitimate.
- Unauthorized transactions: Make unauthorized purchases, transfer funds to other accounts, or conduct other fraudulent transactions.
- Identity theft: Commit identity theft by applying for credit cards, loans, or other financial products in the victim's name.
- Credit card fraud: Open credit card accounts using stolen or falsified identities and then using these cards for fraudulent purchases, cash advances, or balance transfers.
Role of bots in banking sign-up fraud
Bot attacks rose an estimated 167% in Q2 of 2023 in comparison to human-driven attacks, which increased 26% in Q3 over the same time period. By automating and streamlining the various aspects of the process, increasing efficiency, and minimizing the risk of detection, bots play a significant role in phony registrations.
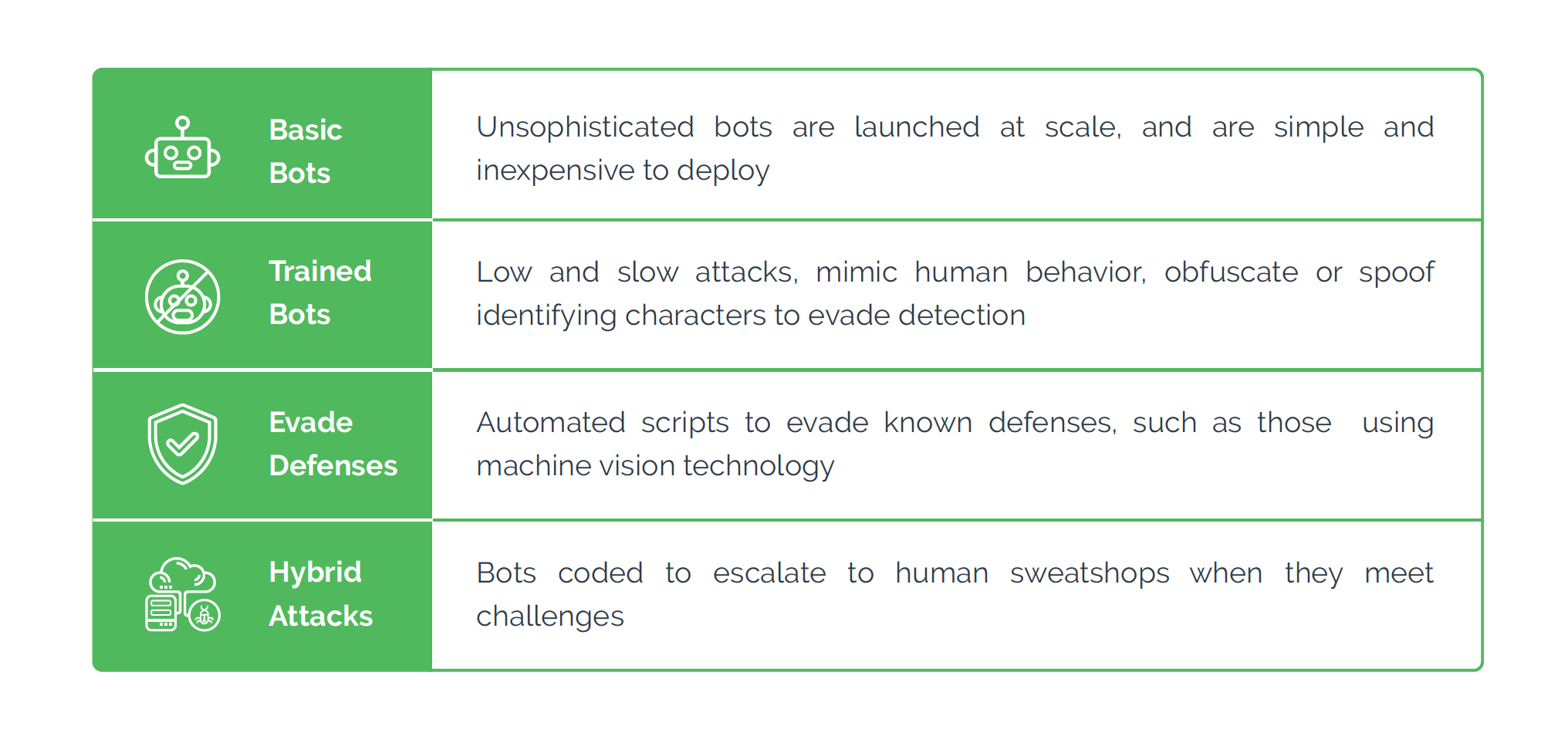
Not only do automated bots attacks make new account fraud faster and more scalable, but they also make detection harder through the following methods.
- Account creation: Hackers can program bots to create multiple fraudulent accounts quickly. Further, programmed bots can fill out online application forms for new accounts using stolen or fake information, navigate through the bank's website, input false information, and bypass security measures such as CAPTCHA challenges.
- Identity verification: Using fake or stolen information that matches the criteria required for approval, bots can manipulate the automated verification systems used to cross-reference user information with external databases for identity verification.
- Transaction automation: Bots can automate transactions such as depositing counterfeit checks, transferring funds between accounts, or making purchases using stolen credit card information to quickly exploit the fraudulent accounts before the bank can detect suspicious activity.
- Phishing and social engineering: Bots have become a popular tool for automated phishing attacks. Using bot traffic, fraudsters can trick users into sharing sensitive information such as login credentials or personal information that can then be used to open new accounts or take over existing ones.
Challenges in banking new account fraud detection
Banking new account fraud detection poses several challenges to security teams. Banks need a multi-faceted approach that combines advanced technology, robust risk management strategies, and ongoing collaboration with industry stakeholders. Some of the common challenges include:
- Identity Verification
- Synthetic Identities
- Fraudulent Transactions
- Regulatory Compliance
- Customer Experience
Red flags
For efficient detection and prevention, banks should be vigilant for red flags such as:
- Unusual identity information: Inconsistent or suspicious identity information provided during the account opening process, such as mismatched names, addresses or contact details.
- High-risk locations: Applications originating from high-risk geographic locations or regions associated with increased fraud activity, or sudden changes in the applicant's location or IP address during the account opening process.
- Unusual account activity: Rapid or unusual changes in account activity shortly after opening, such as large deposits, frequent transfers or suspicious transactions.
- Synthetic identities: Applications containing identity information that cannot be verified through traditional means or exhibit characteristics of synthetic identity fraud, such as the use of fabricated social security numbers or addresses.
- Unsolicited account applications: Unsolicited account applications received via email, phone or other channels without prior contact or interaction with the bank may be part of a phishing or social engineering scam.
- Multiple account openings: Applicants attempting to open multiple accounts within a short time frame using different identities or variations of the same identity information.
- Previous fraud history: Applicants with a history of fraudulent activity, identity theft or suspicious behavior in the banking system.
- Unusual documentation or behavior: Unusual or incomplete documentation from applicants, nervous or evasive behavior during the onboarding process, or refusing to provide additional information or verification when requested.
Technologies for banking account opening fraud detection
Banks can employ various advanced technologies. Some of these include:
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI): Analyze large volumes of data, including customer behavior, transaction patterns, and account opening information, to detect anomalies and patterns indicative of fraudulent activity.
- Biometric authentication: Use biometric authentication technologies such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition or voice recognition to verify the identity of new applicants and ensure that the person opening the account is who they claim to be.
- Behavioral biometrics: Analyze user behavior patterns, such as typing speed, mouse movements and device interaction to detect anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity during the account opening process.
- Document verification tools: Authenticate identity documents provided by new account applicants and detect signs of tampering or forgery using document verification tools equipped with optical character recognition (OCR) and image analysis capabilities.
- Challenge-response authentication: Use smart challenge-response authentication mechanisms such as Arkose MatchKey to stop bots and malicious human fraud farms from exploiting network vulnerabilities or scaling up the attack.
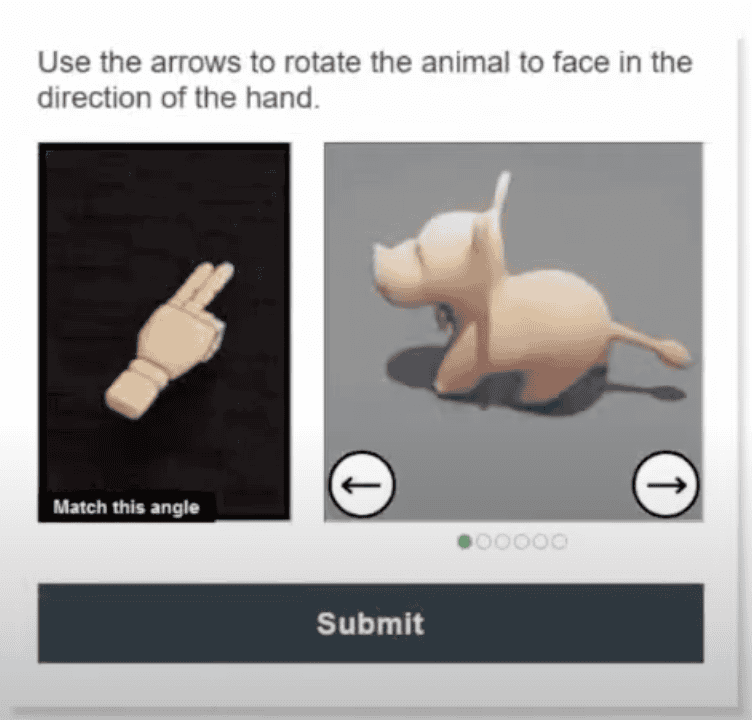
- Geolocation and device fingerprinting: Verify the physical location of new account applicants and detect suspicious activities such as account access from high-risk locations or multiple account openings from the same device.
- Transaction monitoring systems: Monitor account activity for unusual patterns, such as large or unusual transactions, frequent transfers or account access from unfamiliar locations with transaction monitoring systems equipped with real-time analytics capabilities.
- Digital identity solutions: Verify and authenticate the digital identities of new account applicants while ensuring data privacy and integrity.
- Fraud detection platforms: Invest in comprehensive banking new account fraud detection systems that integrate multiple detection techniques, such as rule-based systems, anomaly detection, machine learning models, and behavioral analytics.
- Customer risk profiling: Develop new customer risk profiling models using predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms to assess the risk level associated with each applicant based on factors such as demographic information, transaction history, and behavioral patterns.
Want to learn more about how bot detection and mitigation software can help your financial services institution prevent fake account registrations and other crimes like account takeover fraud? See how Arkose Labs helps you protect against new account fraud.